Delivery routes are adjusting in real time. Warehouses operate with minimal human intervention. AI-powered analytics are forecasting disruptions before they even occur.
This is not a distant vision; it’s today’s reality. As logistics becomes increasingly complex and competitive, Artificial intelligence is emerging as a powerful catalyst for transformation. From predictive maintenance and route optimization to warehouse automation and last-mile delivery, AI is streamlining operations at every level.
According to recent industry data, AI-driven Solutions like warehouse automation are already cutting operational costs by up to 50% and boosting workplace safety by 90%. These technologies are not only enhancing efficiency but also helping logistics businesses become more agile, sustainable, and customer-focused.
In this blog, we’ll explore how AI is reshaping the logistics industry. From real-world use cases to cutting-edge products and future-forward trends that are redefining the way goods move, warehouses function, and supply chains respond. Whether you’re a logistics leader, tech innovator, or just AI-curious, this is your roadmap to a smarter, faster, and more resilient logistics ecosystem.
Challenges Faced by the Logistics Industry In 2025
The logistics sector in 2025 is a world of complexity and confusion – traffic congestion, erratic customer demand, lack of visibility across numerous supply chains, and growing inventory. With customer demand for quicker, more transparent deliveries increasing, logistics companies need to change the way they have traditionally worked to smarter and more resilient solutions. Here are some of the biggest hurdles faced by the logistics industry.
1. Conventional Route Planning
When it comes to logistics, it is all about arriving on time, and to arrive on time, you have to plan your route carefully. But there’s more to finding the shortest path than simply traveling from point A to point B. Last-minute obstacles—automotive traffic jams, road blockages, and extreme weather—can turn any delivery into a logistical nightmare.
This is where route optimization tools powered by AI are useful. These intelligent systems, which analyze massive real-time streams of traffic data, delivery time slots, road conditions, and vehicles’ load capacities, etc., can assist logistics companies in determining the shortest and most fuel-saving path of the routes. The result? Faster delivery times, less fuel consumption, fewer delayed arrivals, and lower operational costs in general.
Given customers’ demand for instant gratification and delivery—and often, faster than ever before—AI for dynamic route optimization is not just a differentiator but an increasingly expected capability.
2. Limited Real-Time Visibility in Supply Chains
Real-time location tracking and monitoring of shipments has always been one of the bottlenecks in the Supply Chain Management (SCM). When businesses cannot track their shipments or gain visibility into their status, there are blind spots in decision-making, response times suffer, and inefficiencies are created, which are expensive to fix.
To counteract this, companies are utilizing advanced monitoring systems: IoT-enabled sensor technology and GPS tracking. They allow real-time tracking of where inventory is in the supply chain, what type of shape it is in, and how it is moving along the supply chain. Companies can plan more accurately and take swift action on delays or other issues in real-time, and more effectively forecast and manage their inventories. And, of course, the better sightlines add up to smarter logistics, improved customer satisfaction, and a more resilient supply chain.
3. Inventory Management Challenges
Logistics is, in many cases, still confronted with inventory management problems. Businesses have to strike a balance, keeping only enough on hand to satisfy customer demand without overstocking, which would risk tying up capital in unsold inventory. That’s particularly difficult to strike in industries with seasonal demand, erratic supply chains, or fickle consumer behaviors.
And to address that challenge, an increasing number of logistics-focused enterprises are adopting smart Inventory Management Systems that are based on AI and data analytics. Retailers such as Walmart, for example, use predictive algorithms that analyze sales data, regional sales trends, and even weather forecasts to determine where best to stock warehouse inventory. These are advanced systems that allow better demand forecasting and the automation of reordering so that you have a lower risk of overstocking or stockout.
Cloud-based platforms such as NetSuite, Zoho Inventory, and Oracle SCM are also in many business shortlists that want to consolidate inventory data, monitor its movement in real-time, and connect to e-commerce and/or POS systems. By applying these techniques, firms are able to reduce holding costs, enhance order fill rates, and optimize their overall supply chain performance.
4. Demand Forecasting And Accuracy
Effective demand forecasting is one of the crucial issues in the field of logistics. Indeed, one mistake can disrupt the supply chain, and the consequences are equally grave.
Retailers, for example, tend to overstock cold-weather merchandise like clothing and gear in anticipation of heavy seasonal demand, and then find themselves taking markdowns that reduce their profits and paying to store the excess inventory when the weather turns out to be milder than the models had suggested. But at the outset of the pandemic, many companies were surprised by how quickly demand for those kinds of basic goods — sanitizers, masks, and the like — surged, leading to critical shortages and missed revenue.
Conventional forecasting methods often fail to take account of the rapidly changing consumer preferences, new emerging market trends, and the exterior, like geopolitical risks and adverse weather. As a result, companies experience a great deal of waste due to the misalignment of supply with demand, wasted resources, and dissatisfied customers.
In hyper-speed categories such as fashion, consumer electronics, and FMCG, these forecast inaccuracies can be even more dangerous, as they can mean lost market share and reputational damage. To stay ahead, companies need not just historical analysis but real-time response, something traditional forecasting tools alone may not deliver.
For fast-moving sectors such as fashion, consumer electronics, and FMCG, these forecasting inaccuracies can have particularly damaging consequences – loss of market share and reputation damage. Remaining ahead demands more than backward-looking analysis; it requires a real-time response that traditional forecasting tools alone cannot deliver.
5. Sustainability Issues
Sustainability is still one of the biggest issues in contemporary logistics. Logistics companies are under greater pressure to be seen to do their bit for the environment as regulations become stricter and consumer demand for greener solutions continues to increase.
The industry has been denounced for contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly through long-haul trucking and air freight, and wasteful last-mile deliveries. For instance, in urban areas, pollution and traffic are significantly affected by the delivery flow of goods itself, leading to the quality of air in those cities, but also the bad perception from local citizens, which leads to the creation of anti-logistics hubs.
How AI In Logistics Can Help The Industry?
While we remain several years away from fully autonomous fleets, the real-world applications continue to not just provide futuristic promise, but rather to provide the necessary equipment to change operations from the base up. The potential for cost savings and improved accuracy and service that were previously unimaginable is already enticing logistics companies with AI for everything from predictive maintenance to intelligent network designing.
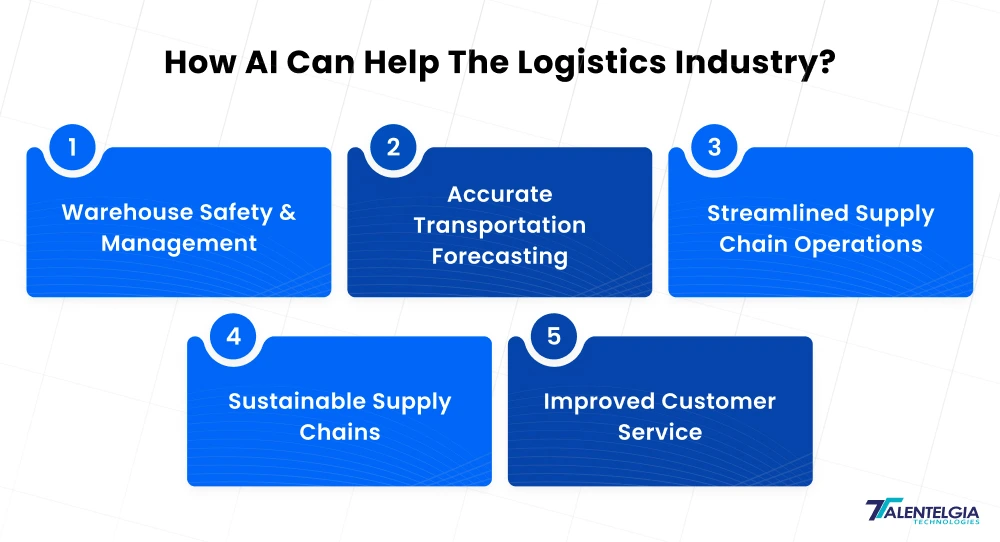
Here are some of the most influential and applicable AI use cases in logistics that are already providing measurable value:
- Warehouse Safety & Management
Safety in high-traffic, fast-paced warehouse operations remains at the forefront of challenges for the logistics and supply chain professionals we serve. Given the use of heavy equipment, human labor, and enormous amounts of inventory, they come into contact with each other daily. The chances of accidents are still pretty high, such as slips, trips, and falls, to incidents related to equipment misuse.
The system often lacks reliable monitoring of the safety protocols and real-time insight into the warehouse state, particularly in older networks. For example, many facilities still rely on antiquated means of manual or disjointed processes that make it challenging to identify hazards or require adherence to an inspection schedule.
Also, bad stock handling, shelves overloading, and or the equipment not kept properly maintained can enhance the possibilities of working failure and cause the worker to be injured. In an environment of tired and overworked employees, repetitive motion, and high-stress deadlines, such a lapse in attention could easily lead to a catastrophic safety moment or legal liability.
- Accurate Transportation Forecasting
Unpredictability taints transportation planning time and time again. Whether it’s rising freight rates, changing customer demand, tightening carrier capacity, or seasonal disruptions, which lead to a lousy demand forecast accuracy. Logistics providers also often don’t have visibility into when capacity and shipping prices fluctuate, which can lead to last-minute decisions. That may increase costs or cause delays in deliveries. The majority of traditional models rely on static data or historical trends, which cannot respond to the real-time market.
This could result in over- or underbooking of transport assets, missing shipping windows, or squandered cost savings. Organic events, like an unexpected spike in fuel prices or labor shortages in an area, can disrupt months of planning on the part of logistics managers, leaving them scrambling to react to a series of fires. With no ability to understand the future availability and price curve for transportation, supply chains are exposed to potential slowdowns, escalations, and unhappy customers.
- Streamlined Supply Chain Operations
Artificial intelligence is changing the way supply chain and logistics managers work, including here at Insight, thanks to AI-driven simulations and digital twin technology.
With the power of AI, companies can now simulate intricate logistics networks without any real-world interference. By using simulations, which are often run with the help of digital twins (virtual 3D replicas of factories, warehouses, or product assemblies), planners can test alternative scenarios, such as what happens when capacity increases at one location, A, or at one location, B, without creating a real-time disruption.
AI accelerates these simulations while also making them smarter. Simulations are much better and more informative than your typical planning tools when machine learning algorithms dictate which model you select and in what order the workflow is performed.
And it’s not confined to three-dimensional environments. AI also allows 2D process simulations to display and run what-if scenarios around other changes, such as suppliers or new deliveries. This enables the logistics department to quickly detect the most efficient processes, reduce delays, and minimize operational costs, all while staying nimble in a rapidly changing international marketplace.
- Sustainable Supply Chains
Among the most effective uses of AI in today’s supply chain is to enhance sustainability. Thanks to automation in a smarter way and data-driven optimization, AI can help organizations lower their carbon footprint and overcome environmental responsibilities better than ever before.
One such use case is AI-based route optimization tools that make use of traffic data, fuel consumption patterns, and delivery timings to optimize routes to minimize fuel usage and emissions. Reducing empty truckloads (a truck is returning empty from where it just delivered a load) and optimizing delivery routes equals less energy wasted, in other words.
You can use machine learning in production planning to prevent overproduction and reduce product spoilage. By analyzing past data on inventory, present-tense projections of demand, and even the status of equipment maintenance, manufacturers can make precisely what is needed, no more, and no less.
- Improved Customer Service
AI chatbots are now more critical in driving customer service in modern supply chains. Virtual agents are available to assist customers at any time and, with that immediate, 24/7 support, are able to check on their orders, get estimated delivery times, and stay updated on the status of their delivery without the hassle of long support lines.
Customers no longer need to wait on hold for a human to answer basic questions, including where an item is or how long a delivery will take: AI-driven chatbots can quickly address availability, shipping, returns, and more, enhancing the entire shopping and fulfillment process.
One of the best examples of this is UPS’s AI-powered chatbot, UPS Bot, that assists users in tracking shipments, receiving rate quotes, and managing common questions, all using a straightforward, natural chat experience.
More than just customer serviceEssentially, then, AI chatbots aren’t just a customer service tool; they’re a key part of creating a faster, more responsive, and self-service-driven supply chain.
AI In Logistics Use Cases
As artificial intelligence continues to make inroads into every facet of logistics, its real-world applications are proving to be more than just futuristic promises—they are essential tools transforming operations from the ground up. From predictive maintenance to intelligent network design, AI is helping logistics companies cut costs, boost accuracy, and improve service in ways that were previously unimaginable. Below are some of the most impactful and practical use cases of AI in logistics that are already delivering measurable value:
1. Predictive Maintenance
AI goes beyond manufacturing—it’s also a significant part of IT infrastructure.
When a server shows signs of slowing, network traffic spikes unexpectedly, or a breach appears imminent, AI tools notify the IT staff immediately. And this early warning could prompt preventive actions such as upgrading software, hardening weak endpoints, or replacing faulty hardware, all before a crash results or data is lost.
For organizations with critical digital platforms, predictive maintenance delivered by AI provides:
- High uptime
- Improved customer experience
- Reduced operational costs
Here’s how some of the top firms are putting this into practice:
- Siemens: Monitors their industrial equipment with AI. Smooth Maintenance Strategy has considerably reduced the incidence of breakdowns and repair expenses.
- General Electric (GE): Uses AI models to analyse how jet engines are performing and predict when parts will need servicing, enhancing the safety of the aircraft and its overall performance.
- Shell: Leverages AI to anticipate when equipment in oil and gas plants needs maintenance, minimizing downtime and increasing productivity.
2. AI For Route Optimization
AI is transforming how logistics firms plan and execute deliveries. By taking into account real-time parameters such as traffic, road conditions, weather, load of the vehicle, and urgency of delivery, AI-powered solutions assist in determining an optimized delivery route, saving travel distance, reducing fuel consumption, and ensuring fast delivery without affecting the customer experience.
The most potent thing about AI is that it can also learn on the fly. Unlike static routing mechanisms, AI adapts to live feedback and reroutes vehicles on demand as traffic jams, blocks, or weather disturbances happen in real-time. This on-the-fly decision-making not only cuts downtime, but it’s increases fleet utilization, decreases the need for more vehicles, cuts costs, and significantly reduces the environmental footprint. In short, AI-based route optimization is helping businesses achieve last-mile delivery that’s smarter, faster, and more sustainable.
AI-Driven Route Optimization Examples in the Real World
- FedEx: Using sophisticated AI planning tools, FedEx eliminated more than 700,000 daily delivery miles by optimizing routes for efficiency at scale, saving fuel and time on the road.
- P&O Ferrymasters: This logistics provider used AI to maximize ship loading, resulting in a 10% increase in cargo capacity, massively winning on space, cost, and efficiency.
3. AI in Logistics Network Design
AI is transforming logistics network design, taking it from smart and fast to smarter, faster, and cheaper. Instead of making educated guesses or using fixed models, AI scours enormous datasets to perfect everything, from where warehouses should be placed to which delivery routes will be the most time and cost‑effective. With this knowledge, companies can be able to create efficient logistics networks that not only result in cost savings but also improve service quality.
For example, an AI System Could suggest moving a warehouse nearer to an area of high demand, immediately reducing the last-mile delivery time and costs of fuel. It can also be used to run thousands of “what-if” scenarios to forecast how a network will perform when conditions change, like seasonal spikes or supply chain disruptions. This clarifies for decision-makers how different changes will affect the performance of the system before they make those changes.
In addition to cost and speed, AI also bolsters long-term resilience. It takes into account variables such as shifting customer demand, geopolitical risk, and disruption from climate change in forming networks that can flex and rebound. The result? Logistics infrastructure that’s not only optimized for today, but future-proofed for tomorrow.
4. Warehouse Robots
Warehouse automation is changing the face of the supply chain in the age of AI-driven robots. These smart machines automate important tasks such as picking, packing, sorting, and inventory, with performance that drives same-day order fulfillment, reduces errors, and cuts labor costs dramatically.
With AI algorithms, today’s warehouse robots can navigate complicated layouts, adapt to the changing demands rapidly, and easily connect to other systems such as WMS (Warehouse Management Systems)or ERP platforms. This translates to more efficient workflows, informed decision making, and, well, a smarter warehouse in general.
Real-World Example: Amazon’s Robotic Warehouses
Amazon is the most notable example of warehouse robots at scale. The e-commerce giant has unleashed over 200,000 robots in its fulfillment centers worldwide. These bots tackle routine, time-sensitive work such as hauling goods, sorting packages, and supplementing order picking in collaboration with human workers.
That has allowed Amazon to process millions of orders, particularly during peak demand, such as holiday sales. By incorporating robotics into their warehouse facilities, they have sped up their operation and optimized resources while keeping the customer happy.
- Smarter Last-Mile Delivery
Last-mile delivery, the last leg of a package’s journey from a distribution center to the customer’s doorstep, has become the most expensive part of the logistics process. The cost of this last stretch of the delivery pipeline has climbed to a massive 53% in 2023, and it soared to 41% of total delivery expense in 2018, reports the CapGemini Research Institute.
With customer expectations for rapid, real-time delivery only increasing, businesses are reconsidering how to fulfill orders. The trend is toward decentralization — ordering smaller delivery hubs, partnering with third-party logistics providers, and, most importantly, AI-driven route optimization technology.
Logistics teams can also leverage AI to instantly route shipments based on traffic updates, vehicle load capacity, delivery windows, customer location, and other time-sensitive information. AI algorithms can also enable drivers to make on-the-fly adjustments when faced with unplanned delays, such as road closures or traffic, which can increase reliability and result in satisfied customers.
By employing AI in last-mile planning, companies are able to reduce fuel costs, accelerate deliveries, and remain competitive in a rapidly changing logistics industry.
- Boosting Workplace Safety with AI-Powered Computer Vision
Computer vision is revolutionizing safety at work in the warehouse and factories. By recording and processing live footage, AI vision systems can monitor human and vehicle motions, flag potential dangers, and recognize ergonomic shortcomings that can result in chronic injuries or workflow drag.
Advanced visual analytics enable logistics managers to draw upon data insights to make decisions about traffic hot zones and stockpiling clogs, the latter of which can cause loss of perishable inventory. This helps teams manage inventory placement, refine aisle configuration, and reduce accidents between equipment and staff.
Apart from being an efficient system, the AI-based surveillance monitors also help in site security. These intelligent systems can quickly detect unauthorized access or abnormal actions, sending notifications to help prevent theft, vandalism, or security breaches in real time.
By interweaving computer vision into warehouse activities, businesses can lower the number of accidents, increase compliance, and foster a safer and more productive space for workers.
Top AI-driven Logistics Products
As logistics operations become more complex and customer expectations rise, AI-powered tools are stepping in to streamline supply chains, optimize routes, and enhance real-time decision-making. A number of cutting-edge products are leading this shift, offering intelligent solutions for last-mile delivery, autonomous transport, predictive planning, and supply chain resilience.

Here are some of the top AI-driven logistics products transforming the industry today:
1. DispatchTrack
DispatchTrack is revolutionizing the last mile with the industry’s first intelligent dispatch solution for hybrid routing and real-time tracking. With sophisticated machine learning algorithms, the solution is able to optimise thousands of delivery routes within a few minutes, making fleet management more efficient and improving customer satisfaction.
One feature that makes DispatchTrack especially unique is its predictive ETA engine, which always delivers with as high as 98% accuracy, using an evolving predictive model that learns from real-time data, such as traffic conditions, driver behavior, and service time. The system can also adjust routes dynamically with the capability to be overridden (manually) so drivers have control and flexibility in ever-changing conditions.
Leveraging the combination of fast, precise, and flexible delivery, DispatchTrack enables businesses to create perfect delivery moments, orchestrate all customer delivery interactions, and automate mission-critical last-mile aspects of the delivery service, while achieving 100% visibility in real time.
2. Nuro’s Autonomous Delivery Vehicles
Nuro develops AI-powered self-driving vehicles for the last-mile local delivery, reshaping local commerce, and achieving a sustainable future through zero congestion and zero emissions. The self-driving delivery trucks will help increase the efficiency of the last stretch of the delivery process, lessening the number of drivers required — both human and electric — on the road. Nuro’s unmanned delivery chassis on city streets looks like a promising leap forward for the future of last-mile logistics.
Nuro’s fully autonomous vehicles use AI to maneuver through tough urban environments, making deliveries more efficiently and reliably. This creative method not only improves working efficiency but also offers a new solution for last-mile delivery to the logistics enterprise.
3. IBM Watson Supply Chain
IBM Watson Supply Chain uses advanced AI and machine learning algorithms, which provide support in order for companies to better manage operations, predict behaviors, and align supplier relationships. This smart platform provides visibility at a glance throughout the supply chain with predictive insights and recommended actions right at decision-makers’ fingertips.
By ingesting data from complex systems, such as inventory, market trends, and supplier inputs, Watson helps companies proactively identify risk and disruptions before they hit the news, improve inventory accuracy, and use automation to streamline logistics. The company’s AI-guided platform makes better, faster decisions that mitigate risk and lower the cost of supply chains.
Companies achieve a competitive advantage with IBM Watson Supply Chain Insights by:
- Sophisticated inventory management and forecasting demand
- End-to-end supply chain transparency
- Proactive intervention to avoid disruption and tactical planning
This position is to be the standard choice for durable, data-capable, and future-state supply chains.
4. Oracle Supply Chain Management
Oracle Supply Chain Management (Oracle SCM) is an excellent AI-enabled collection of logistics and operations tools created to enhance every part of the supply chain. Built for companies that demand agility, scalability, and accuracy, Oracle SCM provides full visibility across the supply chain and the insights companies need for data-driven decision-making, powered by leading-edge technologies like AI, IoT, and support for blockchain.
This smart platform improves supply performance by providing custom modules such as:
- Oracle Intelligent Track and Trace – Tracking and tracing shipments, as well as carrier routes, in real time with AI support.
- Oracle Demand Management – Get the right demand to the right place at the right time and stock levels to better meet demand.
- Oracle Supply Chain Planning – Supporting organizations in building more resilient and adaptive supply plans with predictive analytics.
- Oracle Transportation Management – Optimizes the transportation of goods and cost-effectively increases transportation service efficiency.
- Oracle Warehouse Management – Improves warehouse control and delivers the ability to maximize inventory location movement, space usage, and shipping precision.
Future Of AI In Logistics
As logistics becomes more complex and customer expectations continue to rise, artificial intelligence is playing an increasingly critical role in transforming supply chain operations. According to recent industry forecasts, the AI in logistics market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate CAGR of 25.9% between 2025 and 2034, reflecting its expanding impact across transportation, warehousing, and delivery systems:
- Self-Driving Trucks and Truck Platoon for Long-Haul Freight
The most revolutionary AI freight logistics application is autonomous trucking. These unmanned trucks help reduce dependence on human labor and increase delivery accuracy. Logistics companies are experimenting with AI-driven truck platoons, trucks that travel in close convoy with minimal gaps. That’s a drastic reduction in aerodynamic drag, fuel consumption, and carbon emissions, resulting in an energy-saving and cost-effective freight transportation solution.
- Efficient Routing with Consolidation of Load
AI delivers improved route optimization for shippers by analyzing vast amounts of data, such as weather, congestion, road closures, and delivery windows. This results in dynamic route selection to use the minimum fuel, time delay. Simultaneously, AI-powered load consolidation algorithms drive trucks to maximum weight by smartly aggregating deliveries, slashing non-value-generating transport, and bringing down transportation costs and emissions even more.
- Smart Warehouses
As Artificial intelligence evolves, smart warehouses are becoming the mainstay of next-gen logistics. Powered by AI-enabled automation and robotics, these intelligent facilities automate basic warehouse functions from inventory management to order picking.
Shortly, companies will use automation to complete repetitive, unattractive jobs, such as picking, packing, sorting, and stock replenishment, including labor, as conveniently. AI algorithms are able to prove and optimize workflows through real-time data analysis, minimizing human error and augmenting overall operational productivity. This transition allows for higher speeds, lower operating costs, and even more accuracy in high-volume fulfillment applications.
With advances in smart sensors, computer vision, and robotics in harmony, AI-powered warehouses are not just increasing efficiency — they are disrupting how supply chains operate in the digital age.
- Hyper-Personalization in Delivery
Artificial intelligence is redefining customer experience in logistics through hyper-personalization. As AI technologies advance, businesses can offer delivery services tailored to each customer’s unique preferences and real-time needs.
From dynamic delivery windows and preferred drop-off points to real-time notifications, AI systems can analyze customer behavior and historical data to craft a delivery journey that feels effortless and intuitive. Machine learning algorithms track preferences, optimize scheduling, and even adapt routes based on when and where a customer is most likely to receive a package.
This next level of personalization in logistics not only boosts customer satisfaction but also improves operational efficiency by reducing missed deliveries and rescheduling. In a world where experience matters as much as speed, AI-powered hyper-personalization is setting the new gold standard in last-mile delivery.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing the logistics industry by tackling its most persistent challenges—be it route optimization, inventory accuracy, safety, sustainability, or real-time decision-making. By integrating intelligent systems, companies can unlock greater efficiency, reduce operational costs, and offer seamless customer experiences. From warehouse automation to predictive analytics and personalized delivery, the possibilities are no longer futuristic—they are here, scalable, and already generating measurable impact. As the industry continues to evolve, those who embrace AI-driven logistics solutions today will lead the way in tomorrow’s smarter, greener, and more resilient supply chains.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: