Whenever someone thinks of health care, one of the first things that pops up in our minds is “Doctor’s Office.” However, nowadays, an increasing number of patients are treated, not just by doctors, but also by “Advanced Practice Providers.” The tasks and responsibilities that an advanced practice provider (APP) performs are quite similar to those of a doctor, but not the same.
APPs provide primary and specialized care, and work in emergency medical and acute healthcare clinics and hospitals. They work in various clinical environments and across different states that have varied scopes of practice. In this post, we aim to clarify the types of these roles, highlight the challenges they face, and the ways they treat the patients.
What is APP?
Advanced Practice Providers (APPs) are healthcare and wellness practitioners with advanced degrees and specialized clinical skills that allow them to take on many of the traditional duties of physicians. These professionals have the training and experience to diagnose, treat, and manage many health conditions— they are a vital part of the modern healthcare system.
APPs represent diverse roles, such as:
- Nurse Practitioners (NPs)
- Physician Assistant (PAs)
- Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNSs)
- Nurse Midwives
- Nurse Anesthetists
They are trained in rigorous, postgraduate programmes, typically to the master’s or doctoral level, allowing them to provide high-quality, affordable patient-centred care with a very high degree of autonomy or working in collaboration with physicians.
Why are APPs Important In Healthcare Today?
Patient-centred care consists of disease prevention, health promotion, and patient education. APPs understand the patient deeply because they spend more time with them. They can identify and address a multitude of healthcare needs, and are therefore indispensable members of the healthcare team. These professionals have advanced legal privileges including the assessment and diagnosis, medical prescriptions, and development of comprehensive treatment plans. They all can work independently on various levels and collaborate with other healthcare professionals.
APPs are employed in numerous healthcare environments including clinics, hospitals, and private facilities, and achieve remarkable goal of providing patients with consolidated and comprehensive care. Having APPs in the healthcare system has numerous benefits, including
- Addressing Physician Shortages: With the aging population and fewer physicians, the global healthcare system is experiencing physician shortages. Advanced practice providers (APPs) are instrumental in filling care delivery gaps, notably in rural and underserved areas.
- Enhancing Access to Care: With readily available healthcare services, APPs reduces the patient waiting time and improve access to management of chronic illnesses and other preventive healthcare services.
- Cost-Efficiency: Cost reduction in healthcare delivery is made possible with APPs providing top-quality, evidence-based care for lower fees than physicians.
- Alleviating Physician Workload: With the completion of routine diagnostics and treatments, APPs let physicians to concentrate on complex and specialized cases, improving the efficiency of the healthcare system.
- Improving Patient Satisfaction: With increased time spent with patients, APPs improve the dynamics of the patient-physician relationship. This trust helps with adherence to treatment, improving the health of the population.
What Is the Difference Between APPs and Physicians?
Advanced Practice Providers (APPs) and physicians are both essential healthcare providers but differ significantly in education, scope, responsibilities, and practice autonomy. Below is an elaboration on these differences, along with a comparative table detailing the crucial aspects.
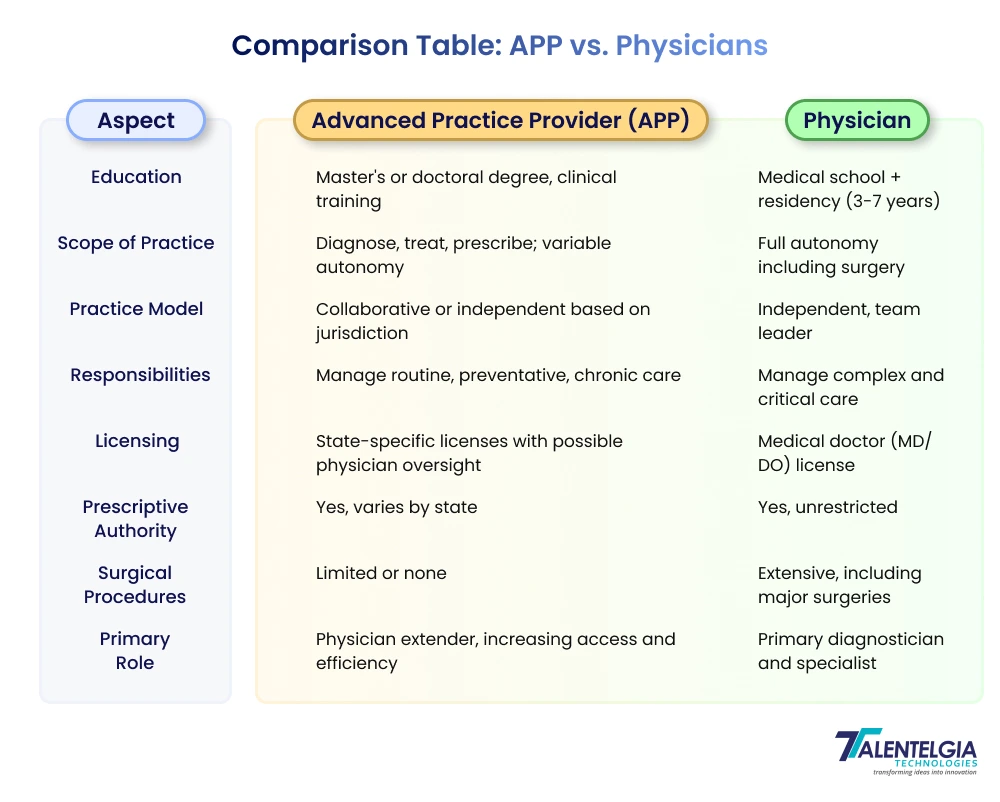
Education and Training
- Physicians complete 4 years of medical school plus a residency program lasting 3 to 7 years depending on specialty.
- APPs typically earn a master’s or doctoral degree in nursing or physician assistant studies and complete clinical training but do not undergo medical residencies.
Scope of Practice
- Physicians have full autonomy and broad responsibilities, including surgical procedures, complex diagnostics, and independent decision-making.
- APPs practice under varying levels of supervision or collaboration depending on jurisdiction but can diagnose, treat, and prescribe medication—often managing primary care independently in many states.
Roles & Responsibilities
- Physicians manage complex cases, surgical interventions, and specialized treatment plans. They lead healthcare teams and provide comprehensive care.
- APPs handle routine and chronic conditions, preventive care, diagnostics, patient education, and follow-up care, acting as physician extenders to increase healthcare access.
Regulatory and Licensing Differences
- Physicians hold medical doctor (MD) or osteopathic doctor (DO) licenses with wide-reaching privileges.
- APPs carry licenses as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, or other advanced clinicians with scope regulated by state laws and institutional policies, sometimes requiring physician collaboration.
Main Types of Advanced Practice Providers

Advanced Practice Providers (APPs) are a highly trained and diverse group of healthcare professionals who have acquired advanced training and clinical training and offer extensive health services. The leading category of roles included in this designation that clinicians are likely to meet in a health care setting is Nurse Practitioners (NPs), Physician Assistants, Clinical Nurse Specialists(CNSs), Certified Nurse Midwives(CNMs) and Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists.
1. Nurse Practitioners (NPs)Nurse Practitioners (NPs) are also referred to as
Also known as “Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs)”, and have graduate-level education, usually at a master’s or doctoral level. They deliver primary care, as well as preventative health services to patients, and are involved in guiding individuals through the diagnosis and treatment of their medical issues. NPs are prepared to practice independently or in collaboration with individuals as a physician provider across the lifespan.
2. Physician Assistants (PAs)
PAs are trained in a medical model, similar to that used for training physicians, but of shorter length and focused on an specific scope of practice (around two years post college or university). PAs diagnose illnesses, develop and manage treatment plans, prescribe medications and may assist in surgery, often working under the supervision of a physician while having considerable independence depending on the practice setting.
3. Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNSs)
Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNSs) are advanced practice nurses whose practice focuses on specific populations or niche areas within each population, such as pediatrics or gerontology. While CNSs might not always be involved in caring for patients directly, their roles in consultation, staff education and clinical policy development are essential.
4. Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs)
Certified Nurse Midwives (CNM) specialize in women’s reproductive care, including prenatal care, labour and delivery, postpartum care, and basic gynaecological services. They also focus on integrated care that supports physical, emotional and social dimensions of women’s health.
5. Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs)
CRNAs are advanced practice nurses specializing in the administration of anesthesia and perioperative care. CRNAs practice in a range of horse-powered settings, such as hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers -> in many rural or underserved areas where anesthesiologists are scarce.
How to Become a Professional Advanced Practice Provider In 2025?
Choosing a career in Healthcare is a career opportunity that demands passion, commitment, and clinical excellence. The path is methodical but highly rewarding, bringing academic performance and practicality together
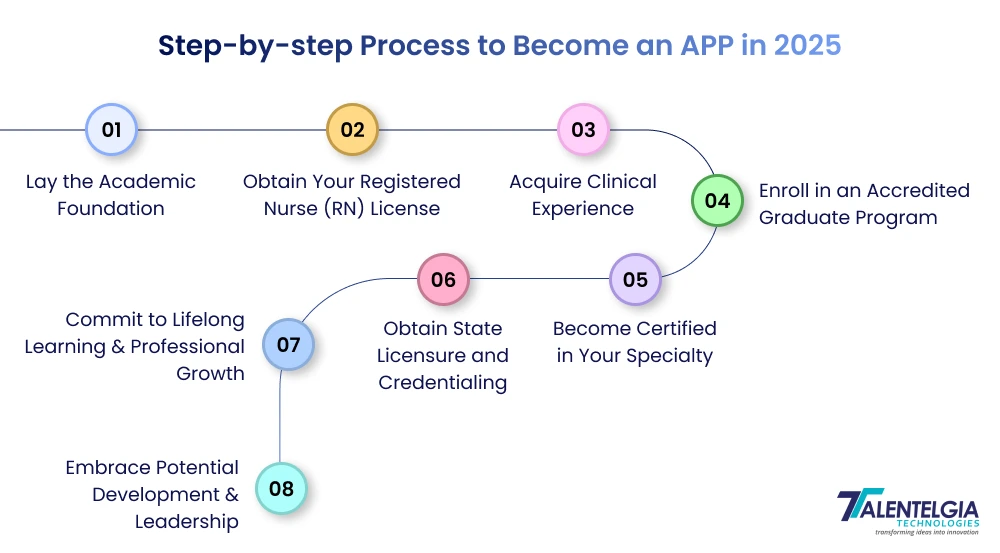
1. Lay the Academic Foundation
Start with a bachelor’s degree — many job seekers earn a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) or another health-related discipline. This essential first phase will develop expertise in fundamental medical disciplines and help you gain exposure to patient care from clinical rotations and hands-on experience.
2. Obtain Your Registered Nurse (RN) License
After a four-year degree, a future APP has to take the licensing test—for nurses, it’s the NCLEX-RN—or similar tests for other roles. This is a license required for clinical work in the “real world.
3. Acquire Clinical Experience
Before advancing in your career, hands-on exposure and clinical experience are critical in diverse healthcare settings. a registered nurse, physician assistant, or other similar roles hone their skills, build clinical judgement, and get themselves ready for advanced practice.
4. Enroll in an Accredited Graduate Program
You have to acquire a master’s or doctorate degree in the APP role of your choice (MPAS for physician assistants, MSN for nurse practitioners). Graduate degrees comprise advanced diagnostic reasoning, pharmaco-therapeutics, leadership, research, and specialty-focused care with hundreds of clinical hours and simulations.
5. Become Certified in Your Specialty
Every APP role mandates appearing for a national certification exam, such as the ANCC, AANP, or NCCPA exam, that justifies clinical knowledge and clinical expertise. It is crucial to clear these tests for individual practice and is often required for employment.
6. Obtain State Licensure and Credentialing
Once certified, you can pursue the license from your state’s regulatory board. Requirements and scope of practice regulations may vary from state to state, so you need to pay close attention to the credentialing process
7. Commit to Lifelong Learning & Professional Growth
APPs are required to continually expand their knowledge, including attending conferences, joining professional societies, and obtaining further certification. For those whose careers are advancing, specialization and leadership roles (like medical director or educator) and contributing to healthcare research are typically part of the journey.
8. Embrace Professional Development & Leadership
With time and experience, APPs can transition to roles like teaching, management, policy advocacy, or consulting. Leadership education, mentorship, and participation in medical organization all prepare them for having a greater impact on the world and their own careers.
Conclusion
There is an increasing demand for APPs with extensive roles in both primary and specialty care. They’re more effective when integrated with telehealth and digital solutions. With ever-changing healthcare workforce demands, training models are changing to retrain APPs for more expanded roles.
Advanced Practice Providers are changing the landscape of healthcare by serving as an alternative to traditional physicians’ care and by providing cost-effective, comprehensive, and accessible solutions. As healthcare advances to meet 21st-century demand, its improved engagement helps patients and providers to serve every individual’s demands in the best possible way. To support this digital transformation, explore our Healthcare App Development Services that empower providers to deliver smarter, more connected, and patient-centric care.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: