There is no denying that the amount of data that companies generate every day is enormous! If you want to make wise choices, identify issues, and run a successful business, transforming your data into actionable insights is required. Business Intelligence (BI), Business Analytics, and Data Analytics are subsets of data management that seek to make historical and current data actionable. A report from Precedence Research shows that the advanced analytics and business intelligence software market was valued at $47.48 billion in 2025, and is projected to hit nearly $151.26 billion in 2034 with a CAGR of 13.74% during the forecast period (2025 – 2034). These statistics clearly show that companies are now harnessing the immense potential of Data.
However, which solution will meet your business needs, and what’s the difference between these terms? There isn’t much difference between business intelligence and advanced analytics, and to make the confusion even worse, they’re often used synonymously with one another. So, before we clarify the difference between them, let’s understand some crucial definitions.
What Is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business Intelligence (BI) is a technology-driven process that transforms raw business data into meaningful, actionable insights to support informed decision-making and improve organizational performance. It combines data collection, integration, analysis, and visualization using tools like dashboards and reports to provide a clear picture of historical and current business operations.
Key Characteristics of Business Intelligence:
- Descriptive Analytics Focus: Primarily answers “What happened?” by analyzing historical and current data.
- Structured Data Usage: Mostly relies on structured data from internal organizational sources.
- Data Visualization: Transforms complex datasets into intuitive charts and dashboards for easy interpretation.
- Self-Service Capabilities: Enables non-technical business users to explore data independently without heavy IT support.
- Performance Management: Monitors KPIs and trends, facilitating timely operational and strategic decisions.
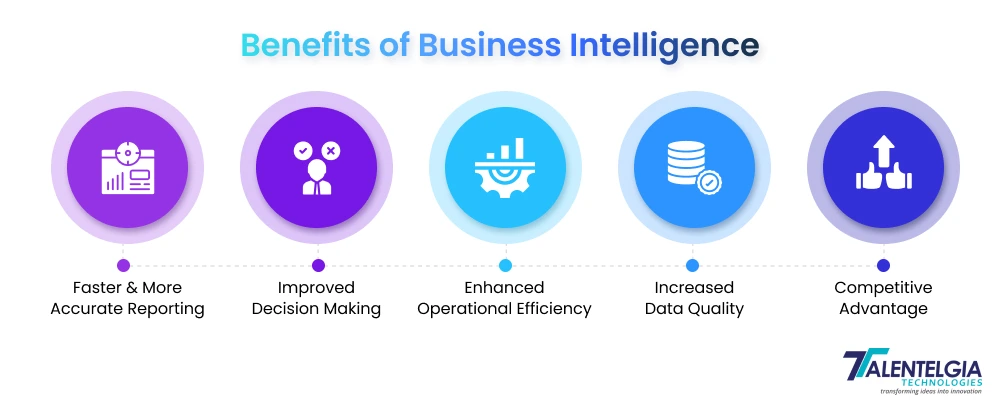
Key Benefits of Business Intelligence
Key Benefits of Business Intelligence
- Faster & More Accurate Reporting: BI tools automate data collection and reporting, providing timely and precise information to stakeholders for quick decision-making.
- Improved Decision-Making: BI empowers organizations to make informed decisions based on comprehensive data analysis, reducing reliance on intuition or guesswork.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies through data insights, businesses optimize processes and resource allocation.
- Increased Data Quality: BI tools help clean, integrate, and enrich data, ensuring that decisions are based on high-quality, reliable information.
- Competitive Advantage: BI enables companies to analyze market trends, customer behavior, and competitor performance, helping them anticipate changes and seize new opportunities.
Purpose and Use Cases of Business Intelligence (BI)
Business Intelligence aims to turn raw data into meaningful insights that support strategic decision-making, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage. It empowers organizations to visualize, analyze, and interpret past and current performance data to make well-informed, data-driven decisions that enhance business outcomes.
Use Cases of BI:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: BI tools synthesize huge amounts of data into clear visual dashboards, enabling fast, accurate, and data-backed decisions across all levels of the organization.
- Operational Efficiency: BI helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and unnecessary costs within processes such as supply chain management, inventory control, and customer service, allowing businesses to streamline operations.
- Customer Insights and Segmentation: Organizations analyze customer purchasing behaviors, preferences, and engagement patterns to tailor marketing efforts, personalize offerings, and boost customer loyalty.
- Performance Monitoring and Benchmarking: BI dashboards track key performance indicators (KPIs) in real time, enabling quick course corrections and strategic adjustments, such as benchmarking store performance or production efficiency across regions.
- Market and Competitor Analysis: BI platforms provide insights into market trends, competitor strategies, and industry benchmarks, helping organizations identify future opportunities and threats.
- Financial Analysis and Budgeting: Companies leverage BI for financial planning, budget tracking, and profitability analysis, ensuring better control over financial health and resource allocation.
- Supply Chain Optimization: BI tools analyze logistics, demand, and inventory data to minimize costs and optimize delivery timelines, reducing stockouts and excess inventory.
- Product and Service Improvement: Data analytics reveal customer feedback, product performance, and usage patterns, guiding innovation, quality enhancement, and development of new offerings.
Also Read: Business Intelligence In ERP- A Comprehensive Overview
What Is Advanced Analytics?
Advanced Analytics refers to the use of sophisticated techniques and tools such as machine learning, predictive modeling, statistics, and data mining to analyze data and generate insights that forecast future trends, identify hidden patterns, and prescribe actions to achieve desired outcomes. It goes beyond describing past events to enable predictive and prescriptive decision-making.
Key Characteristics of Advanced Analytics
- Predictive and Prescriptive Focus: Answers “What will happen?” and “What should we do?” by forecasting and recommending actions.
- Diverse Data Types: Utilizes both structured and unstructured data from multiple sources.
- Complex Techniques: Employs machine learning algorithms, statistical models, simulations, and natural language processing.
- Expert-Driven: Requires skilled data scientists and advanced computational resources.
- Strategic Impact: Helps in risk management, customer segmentation, fraud detection, and driving innovation through deep insights.
Read More: The Future of Big Data Analytics: Trends to Watch and …
Key Benefits of Advanced Analytics
Key Benefits of Advanced Analytics:
- Predictive Insights: Advanced analytics enables forecasting of future trends and behaviors, guiding proactive business strategies.
- Risk Identification & Mitigation: It helps organizations detect potential risks and fraud early, minimizing losses and improving compliance.
- Personalization & Customer Segmentation: Advanced analytics support tailoring products and marketing strategies to specific customer segments for better engagement.
- Innovation Enablement: By uncovering hidden patterns and insights, it drives innovation in products, services, and business models.
- Strategic Decision Support: Advanced analytics provides deep, data-driven insights for complex decision-making beyond historical trends.

Purpose and Use Cases of Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics seeks to uncover deeper insights, predict future trends, and recommend actions based on complex data models, machine learning algorithms, and statistical analysis. Its core purpose is to provide foresight that enables organizations to anticipate changes, mitigate risks, and innovate proactively.
Use Cases of Advanced Analytics:
- Predictive Maintenance: Companies like Penske rely on AI-powered predictive models to forecast equipment failures before they happen, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Customer Churn Prediction: Retailers and service providers analyze customer behavior trends to identify those at risk of churn, allowing targeted retention strategies.
- Fraud Detection: Financial institutions leverage machine learning to analyze transaction patterns and flag potentially fraudulent activities in real time.
- Demand Forecasting: Organizations like Amazon use advanced models to predict product demand, optimize inventory levels, and plan supply chain activities, avoiding stockouts and excess stock.
- Personalized Marketing & Customer Segmentation: Advanced analytics segment customers based on preferences, purchase history, and engagement, enabling highly targeted marketing campaigns.
- Risk Assessment & Management: Banks and insurers predict credit risks, insurance claims, and market risks, supporting better risk mitigation strategies.
- Business Innovation: By uncovering hidden patterns in vast datasets, organizations discover new opportunities, develop innovative products, or disrupt markets effectively.
- Operational Optimization: Advanced analytics analyze complex variables in manufacturing, logistics, and workforce management to optimize resource utilization and streamline supply chains.
Also Read: Integrating AI In Business
BI vs Advanced Analytics: Know Their Difference
Both these concepts serve very different functions, though they’re always most effective when applied together. Using a blend of both neural systems, an organization would be better equipped to understand present and future operation strategies, scope, and more intricate tactics that could be used to strategize and predict components of advanced analytical systems.
Business Intelligence vs. Advanced Analytics: Comparison Table
| Aspect | Business Intelligence (BI) | Advanced Analytics |
| Focus | Historical and current data | Future predictions and recommendations |
| Purpose | Reporting, monitoring, and operational insights | Forecasting, pattern recognition, and decision support |
| Techniques | Querying, reporting, dashboards | Machine learning, statistical modeling, simulations |
| User Base | Business analysts and operational managers | Data scientists and analysts with technical expertise |
| Data Types | Mainly structured internal data | Structured and unstructured from diverse sources |
| Complexity | Relatively straightforward | Highly complex, resource-intensive |
Differentiating business intelligence and business analytics is useful for leaders in picking the right tools and right people to scale their business. This is equally relevant for current and aspiring business students in evaluating the academic and skills required to prepare them for their career of preference.
- Purpose & Focus
- Business Intelligence: Concentrates primarily on descriptive analytics, which enables users to comprehend events that occurred in the past and events that are currently taking place. This involves providing an accurate and thorough overview of the business data in the past and present to aid in the operational and tactical decision-making processes.
- Advanced Analytics: Predicts and prescribes analytics beyond description. It inquires as to what is likely to occur in the future and provides the most appropriate recommendation as to what should be taken to improve the results of the future business. Thus, it enables one to make strategic and future-oriented decisions.
- Data Scoop & Complexity
- Business Intelligence: Focuses mainly on structured data from internal sources (CRM, ERP, Transactional databases). The data models are less complex and focused on producing aggregated reports, dashboards, and visualizations.
- Advanced Analytics: Manages structured and unstructured data from a variety of sources such as social media, IoT devices, sensor data, etc. It is powered by advanced algorithms, statistical models, machine learning, and AI to deliver more in-depth analysis.
- User Base
- Business Intelligence: Targeting a wider audience, such as business administrators, analysts, and operational experts without comprehensive technical knowledge. BI tools tend to be self-service, allowing users to analyze data from user-friendly data exploration tools even without programming knowledge.
- Advanced Analytics: Focused towards data scientists, statisticians, and analysts who possess programming, statistical knowledge, and expertise in machine learning (ML). It is a highly technical domain to build, validate, and interpret sophisticated models.
- Outcome & Insights
- Business Intelligence: Provides reports describing what happened and when/trend analysis/visual dashboards looking at how something happened/what the business performance, and the business status.
- Advanced Analytics: Provides forecasts, simulations, and actionable recommendations to answer why something happened and what can be done to optimize/innovate.
- Technological Tools & Techniques
- Business Intelligence: Uses querying tools, reporting software, OLAP cubes, and data visualization applications such as Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik.
- Advance Analytics: Uses machine learning libraries (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch), statistics software (e.g., R and SAS,) data mining tool,s as well as natural language processing and predictive model development algorithms.
- Implementation & Investment
- Business Intelligence: Implementing Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) solutions tends to take less time and resources and is usually less complex. This is because the integration is seamless with the business applications you already have on hand.
- Advanced Analytics: This is the more complex and expensive option. It is more complex because deploying requires the investment of a considerable amount of resources into high-performance cloud computing, infrastructure, and analytical models that are constantly being trained and validated.
- Business Impact & Strategic Value
- Business Intelligence: Aims to achieve operational efficiency, improve accuracy in reports, and make effective decisions driven by reliable data from the past.
- Advanced Analytics: Drives innovation by predicting the future and detecting new opportunities in the business, optimizing risk, and personalizing customer interactions.
Conclusion
In the current business landscape, merging analytics and business intelligence tools provides not only comprehensive insights and visibility but also drives strategic and operational efficiency, improving the business's ability to capitalize on opportunities and maintain a competitive presence in the market.
At Talentelgia Technologies, we focus on providing specialization to help transform your business by leveraging these tools. We focus on providing fully managed and on-demand microservices to help manage CRM systems, lead nurturing, and pipeline management, so that your business's sales operations become effective and efficient.
Connect With Expert Developers Today!


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: