The Internet — one of humanity’s greatest inventions — allows businesses of all shapes and sizes to operate from anywhere, at any time. It also lets companies access new and larger markets and utilize computers to work more efficiently. Whether they want to adopt cloud computing, communicate via email, or just maintain their professional website, cybersecurity should be a priority regardless of the company’s size.
Cyber attacks have become the most common form of fraud and have even outpaced physical theft. Every business that operates online has the responsibility to cultivate an atmosphere of security that improves business and consumer confidence. Online security issues not only affect major companies or organizations, but small and medium businesses(SMBs) as well. As a matter of fact, small businesses are more vulnerable to cyberattacks owing to their limited funds and resources.
Cybersecurity is an ever-changing landscape, and knowing where to begin to protect your business could be daunting. However, it’s essential to defend your business and its other valuable assets against cyber attacks. This guide is designed to help small and medium businesses better understand the cyber world.
An Overview of Cybersecurity for SMBs: Types & Importance
If you think hackers and cyber criminals are only got their eyes on big companies, you’re deeply mistaken! Giant corporations may grab the headlines with their moneybags, but because smaller businesses often don’t have advanced defences like large organizations, they often serve as a low-hanging fruit for cybercriminals.
According to a recent report from Statista, nearly 3,158 cases of data compromises were reported in the USA in 2024, and over 1.35 billion individuals were affected by data compromises that included data breaches, leakage, and exposure. Another report from IBM revealed that the average cost of a data breach is around $4.88 million.
Misconception: “We’re too small, nobody will target us.”
Truth: small and medium businesses are the top targets of cybercriminals.
So, if you’re an owner of a small business, how do you safeguard your hard-earned reputation, sensitive data, and very survival in this digital jungle? Let’s discuss.
What Is Cybersecurity?
At its core, cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computers, networks, software, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage. Just as you lock your doors and keep your valuables secure, cybersecurity locks down your business’s digital “home” against online intruders and digital disasters.
Cyber criminals typically have three approaches: try to access, modify, or destroy sensitive and confidential information. Their main goal is money extortion, changing the business policies of competitors or disrupting business entirely. The protection of business data and information from breaches by competitors has become one of the significant fields of operation.
The crucial information can be stolen and used by competitors with weakening or absent security systems of a business, which is why all efforts should be made to protect the sensitive systems of a company. Without proper cybersecurity, the business is always at risk, so top-security systems have to be in place.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats for Small and Medium Businesses
Small and medium businesses face a shifting landscape of cyber risks. Here are the most common, dangerous, and fast-growing threats that every SMB must be aware of:
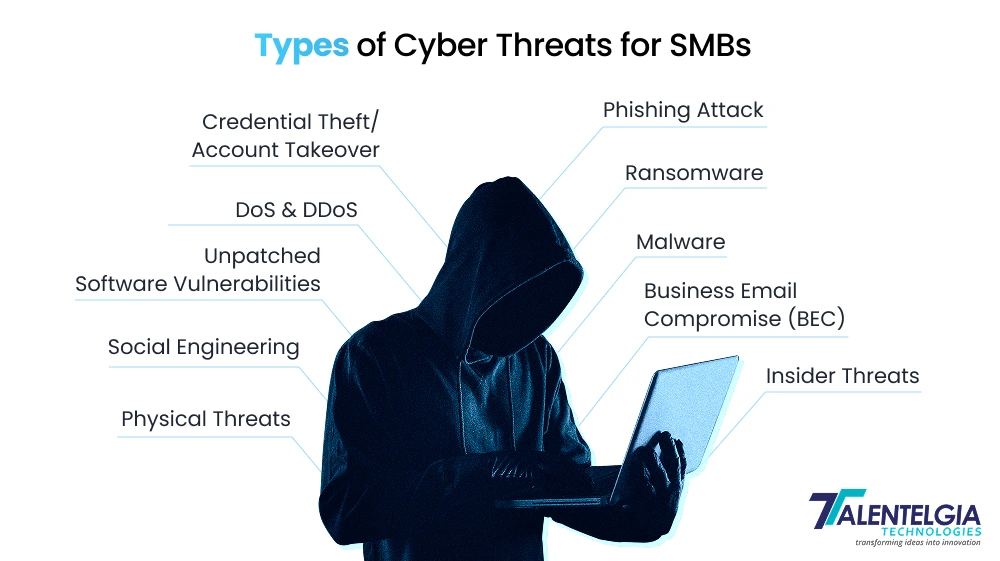
1. Phishing Attacks
Fake emails or messages designed to trick employees into revealing passwords, financial info, or clicking on infected links. Phishing remains the #1 way hackers breach businesses.
2. Ransomware
Malicious software that locks your data or systems until you pay a ransom. Small businesses are often targeted because they may pay quickly to get running again.
3. Malware (Viruses, Trojans, Spyware)
Harmful programs that sneak onto your devices, stealing data, damaging files, or giving criminals a backdoor into your network.
4. Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Attackers impersonate company leadership or key employees to trick staff into sending money, sharing confidential data, or clicking on malicious links.
5. Insider Threats:
Risks from within your organization—disgruntled staff, ex-employees with leftover access, or accidental leaks from well-meaning team members.
6. Credential Theft/Account Takeover
Stolen passwords can allow attackers to access sensitive systems, steal money, or launch further attacks using your company’s name.
7. Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
Overwhelming your business’s website or services with a flood of junk traffic to disrupt operations or extort money.
8. Unpatched Software Vulnerabilities
Hackers exploit outdated programs or operating systems that haven’t had recent security updates, slipping through cracks left open by neglect.
9. Social Engineering
Attackers manipulate people—sometimes over the phone, in person, or online—to gain sensitive information, access, or even entry into offices.
10. Physical Security Threats
Theft of laptops, external drives, or paper records can lead to digital breaches if devices aren’t properly secured or encrypted.
Why Is Cybersecurity Important for small and medium businesses?
You might think, “My business is small—why would anyone target me?” Unfortunately, small and medium businesses are increasingly in cybercriminals’ crosshairs for 6 big reasons:
- Protecting Valuable Data
Even small businesses store vital customer and company information—financial records, contracts, employee data—that must be kept confidential and secure.
- Maintaining Customer Trust
Customers need to feel their information is safe with you. A single breach can damage your reputation and send clients everywhere.
- Staying Compliant
Industries and governments have strict rules about how data is handled. Failure to secure sensitive data can result in hefty fines or legal trouble.
- Cost of Cyber Attacks
The financial impact of breaches, ransomware, or data loss can be devastating—often far outweighing the cost of prevention. Many small businesses never fully recover from a serious cyber incident. According to IBM’s Cost of Data Breach 2024 report, the average global cost of breach reached $4.88 million.
- Operational Continuity
Cyber attacks can shut down your operations, block staff from critical systems, and bring business to a sudden halt. Security keeps your business running smoothly.
- Evolution of Threats
Cyber criminals are constantly finding new ways to attack. Ongoing cybersecurity protects you from not only current risks but also upcoming ones, evolving threats.
10 Essential Cybersecurity Tips & Practices For SMBs
As a small business, the threat of a cyberattack may seem overwhelming. Luckily, there are proactive measures to defend your business by following the latest advancements and innovations in business security. Below are 10 essential cybersecurity tips for businesses:
- Educate & Train Your Team
Regularly educate every employee—not just IT staff—about cyber risks. This includes recognizing suspicious emails, avoiding risky downloads, and understanding company policies on technology use. Interactive workshops, simulated phishing campaigns, and easily digestible resources empower staff to stay vigilant against common threats.
- Update Software & Systems Promptly
Outdated software and hardware are a goldmine for hackers. Set systems to install updates and patches automatically or schedule regular maintenance to close vulnerabilities. Don’t forget devices—even printers and routers need updates to stay protected.
- Use Strong & Unique Passwords
Enforce strong password rules (at least 12 characters, a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols) and ban password reuse across accounts. Encourage or require the use of password managers, which generate and keep track of unique passwords for every login, reducing the risks from leaks and brute-force attacks.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA enhances security by making users present two or more methods of verification or a password— like one-time code from a smartphone app or a hardware key, or biometric such as fingerprint or facial recognition, to access sensitive information. Even in cases where a password has been compromised, unauthorized users will not be able to access the system without further verification.
- Backup Data Regularly
Make automatic backups part of your daily routine and store copies securely—preferably offsite or in the cloud, separated (“air-gapped”) from your leading network. Periodically test backup restoration so you’re confident you can recover from ransomware or accidental deletions.
- Limit User Access & Privileges
Follow the “least privilege” principle: only allow employees access to the data and systems truly required for their roles. Review permissions frequently and immediately revoke access for employees who leave or change positions. Further, exercise strict control over the administrative functions of the system and track usage of such accounts closely. This includes stakeholders. This reduces your risk surface dramatically.
- Secure Your WiFi Networks
Change all default settings for your network equipment—usernames, passwords, and network names (SSID). Use strong encryption (WPA3 if available), hide your SSID where feasible, and create a totally separate guest network for visitors so that your main network remains protected from insecure devices. You can also consider using a VPN (virtual private network) service as a cybersecurity service provider.
- Install Firewall & Antivirus
Deploy reputable firewalls – both hardware (at your internet gateway) and software (on individual devices) – to block malicious traffic. Update and maintain antivirus software on every endpoint to detect and remove infected files or suspicious behaviour before they cause harm. According to Cybernews, selecting the best antivirus is essential because top-rated solutions provide stronger and more consistent protection against modern cyber threats. There are many great antivirus tools available, but they only work when you update them regularly.
It will protect you and your organization in real-time and cover all your assets: desktops, notebooks, and even smartphones. Keep in mind that no solution is 100% effective, so you need to use this method in combination with other security measures.
- Develop a Response Plan
Develop an easy-to-follow, written plan outlining precisely what to do if you suspect or suffer a cyber incident. This should cover steps like containing the breach, informing relevant teams, contacting experts, and communicating with customers. Hold tabletop exercises at least annually so everyone knows their role in an emergency.
- Stay Updated on the Latest Cyber Threats
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, with hackers developing new tactics every day. To keep your defences strong, it’s crucial to stay up to date on the latest vulnerabilities, attack methods, and security best practices. Follow trusted cybersecurity news sources, subscribe to alerts from security organizations, and participate in industry forums or webinars.
This knowledge helps you anticipate risks and adapt your security policies before problems arise. Staying informed empowers your business to respond proactively—not just reactively—to emerging cyber dangers.
Many SMBs are rolling out AI assistants and customer-facing chatbots. Treat LLM-powered apps as part of your attack surface: risks include prompt injection, data leakage, model theft, and insecure outputs that can expose sensitive data. For a concise framework on governance and controls—input validation, content filtering, access controls, adversarial testing, and secure deployment—see LLM Security for enterprises. Applying these practices early will help you ship AI features safely and stay compliant as regulations evolve.
Also Read: Cybersecurity Companies in India
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is essential for all businesses and organizations, and small and medium businesses are no exception. These cybersecurity measures for someone running a small business can be significantly improved with required employee training, establishing and maintaining a persistent culture of cyber hygiene, and securing network and data assets. Aside from significantly improving the overall security, these actions may allow your organization to qualify to obtain or renew a cyber insurance policy.
Are you looking to secure your website or other essential business asset? Let us help you!


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture
















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: