AI-Assisted Development is quickly changing the way software is developed, tested, and maintained in today’s world. Manual coding and debugging that used to take hours can now be fast-tracked with intelligent code suggestions, automated testing, and real-time AI-assisted error detection. With increasing pressure to accelerate release cycles and elevate code quality, artificial intelligence is an indispensable collaborator in the journey from packet to product.
It’s no longer just an advanced autocomplete in 2026 for AI-assisted software development. Sophisticated AI code companions can write whole functions, help refactor your old, insecure legacy code, and even make sure that developers follow best practices more often than not. Development teams are using the AI-enabled tools to increase productivity and lower operating costs across companies ranging from startups to enterprises.
But as it gains traction, AI-Assisted Development has a set of important trade-offs. Quality of code, adherence to standards, security risks, and overcommitment to automation still keep teams that introduce these tools without practices in check. Knowing both the pros and cons of AI-Assisted Development is important when striving to lay solid, scalable, compliant foundations in software.
This guide examines what the concept of AI-assisted software development really means in 2026, its main pros & cons, pitfalls to avoid, and best practices for ensuring responsible and effective adoption.
What is AI-Assisted Software Development?
AI-Assisted Software Development refers to the use of artificial intelligence tools applied by the developers, assist in creating new software. These utilities serve to assist in writing code, making suggestions for improvement, identifying bugs or errors, creating documentation, and profiling performance. Unlike taking over dev teams, AI becomes a smart assistant that increases efficiency and decreases repetitive manual work.
By 2026, AI will have actually helped improve software development beyond giving you code suggestions, driven in part by advanced AI Integration services. Today’s AI code assistants can contextually grasp requirements, have opinions on coding standards, and plug into IDEs and development pipelines. This allows for faster development cycles, better code quality, and more efficient teamwork, but developers are still fully in charge of the ultimate decision-making and architecture.
Pros of AI-Assisted Development
The AI-Assisted Development brings major benefits for modern software teams, allowing them to improve the speed and accuracy of operations. AI-assisted development is transforming how modern applications are built by improving efficiency, reducing repetitive tasks, and accelerating deployment cycles, similar to how an AI ad generator enhances marketing automation and campaign performance. With intelligent automation and real-time insights, AI assists developers in the development process itself without replacing human experience.
Key Advantages:
- Accelerates development with context-sensitive code completion and helps developers solve problems more quickly
- Enhances code quality: Bugs, security vulnerabilities, and logical errors can be found at a very early stage, when they’re introduced to your system localization.
- Less ad-hoc work, like refactoring, formatting, and documenting, happened manually multiple times.
- Reinforces consistent code style across development teams and projects
- Increases productivity for the developer, reducing time spent on architecture and complex logic
- Facilitates quicker new developer onboarding with guided code suggestions and explanations
- Increases test productivity through automatic testcase/unit tests generation
- Aids performance optimization by recommending more efficient algorithms and code constructs
Cons of AI-Assisted Development
Even though AI-Assisted Development brings speed and ease, it has its own downside. As teams, we must be wary of how these standards are used since wrong style guide adoption can affect code quality, security, and future maintainability.
Key Limitations:
- Possibility of suboptimal or incorrect code generation when no validation is present
- Dependence on AI can potentially degrade a developer’s troubleshooting and critical thinking faculty
- Lack of understanding of either complex domain requirements or business logic
- Potential security risks if AI-generated code is not “understood” thoroughly
- compliance & licensing questions associated with use of AI-generated code
- The quality of results is not uniform, depending on context and input clarity
- Reliance on training data that can be based on obsolete or biased coding techniques
- Hard to blame a mistake. A major obstacle is the difficulty of assigning liability for AI errors.
- High tooling costs and integration complexity for teams
AI code assistant compliance in Software development
AI code assistant compliance concerning software development pertains to policies, controls, and procedures that are in place for the purpose of assuring AI-generated or assisted code satisfies legal, regulatory, security-related, and organizational requirements. Since AI tools have an active role in contributing to source code, it is a best practice for organizations to think of the interventions as part of their workflow rather than optional helper tools.
Intellectual property and licensing are one of the key areas to focus on when it comes to compliance. Data about code patterns may reference AI-assisted patterns that mimic open-source or proprietary code. Dev teams need to make sure that code like this doesn’t infringe on open-source licenses or generate ownership disputes. This calls for clear policies on AI being used responsibly and code review as part of the release process.
Data Privacy and Security Compliance Another major concern is data privacy and security compliance. AI code helpers often take in source code, prompts , and some context. Enterprises need to be cautious that they are not releasing trade secrets, customer data, or proprietary algorithms to the outside world, especially in cloud-based services. Complying with laws like GDPR or HIPAA, as well as industry standards, means enforcing strict data handling and access rules.
Compliance is also about accountability and auditability. Teams need to be able to track AI-assisted changes, know who approved them, and ensure that humans are still responsible for the ultimate implementation. Setting up logging, version control integration, and approval processes is essential for transparency and to reduce legal liability.
The use of AI code assistants responsibly will be different and yet innovative and governed in an adapted way by 2026. Enterprises with disciplined compliance practices can safely exploit AI as a tool to drive development and still trust, secure, and remain in alignment with regulations.
AI Risks in Assisted Software Development
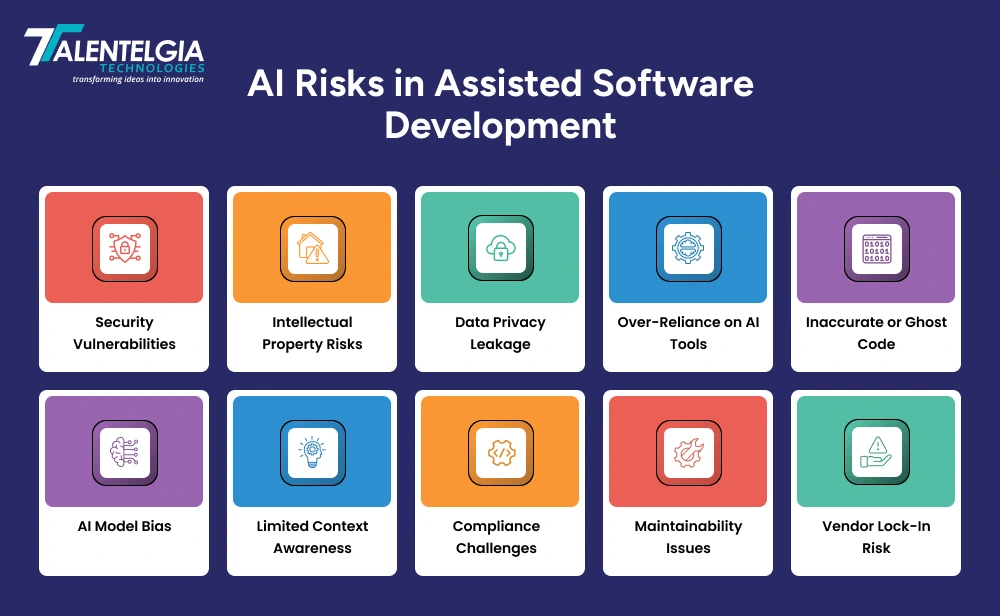
1. Security vulnerabilities
AI-generated code must be scrutinized, or else there may be security holes in the code. AI may indicate things you think are right patterns, but not the best secure code practices, creating the potential for exploits and breaches.
2. Intellectual property risks
There are, of course, IP risks with AI, as assistants can write code that could look almost like open-source or commercially licensed software. This could lead to legal battles and even non-compliant conditions without an appropriate examination.
3. Data privacy leakage
Data privacy leakage is a problem when proprietary source code and/or databases exist with the data rival, especially in cloud-based big data analytics, where mediated knowledge grows by processing data in-house.
4. Over-reliance on AI tools
An overuse of AI tools could dumb down the critical thinking and problem-solving skills of developers, leading teams to rely on automated recommendations without even really understanding why.
5. Inaccurate or ghost code
Erroneous or ghostly code is another potential problem where AI writes syntactically correct code that does not work or breaks down in the real world and contains hidden bugs.
6. AI model bias
AI model bias can shape recommendations after outdated, inefficient, or suboptimal coding practices from training data are learned.
7. Limited context awareness
Limited context awareness entails that AI assistants tend to misinterpret subtle business rules or system constraints, and therefore, the implementation will fall incomplete or incorrect.
8. Compliance challenges
Compliance issues exist if AI-driven code changes are not documented, reviewed, or auditable to maintain compliance with regulatory and organizational standards.
9. Maintainability issues
The issue of maintainability arises when the original developers can’t understand or modify AI-generated code later on, for example, with poor documentation or unclear logic.
10. Vendor lock-in risk
Because tooling is increasingly specific to various platforms, a company whose teams become overly reliant on one AI development platform runs the risk of being locked in by that vendor or suffering service outages, especially as they seek to migrate over time.
Future of AI-Assisted Development
The march of AI-Assisted Development and security tools continues, not just toward greater productivity but also toward smarter, more responsible, better integrated software creation. The future of AI lies in its becoming increasingly ingrained within development workflows, effective at augmenting human expertise and able to respond to complex environments well while also meeting security and compliance requirements.
Human–AI collaboration
We believe the future of AI-assisted development will be defined by more profound human-AI cooperation, and that AI will continue to act as an intelligent aide rather than a substitute for developers. AI tools will no longer just make code suggestions; they’ll increasingly provide architectural guidance, performance optimization, and real-time quality checking to accelerate the development of scalable and efficient systems among teams.
Context-aware and domain-specific AI models
The second major change will be towards context-aware and domain-specific AI models. Future AI assistants will know more about business processes, project standards, and the industry, leading to fewer mistakes from generic advice. This will enable AI-Assisted Development to become more dependable across enterprise and regulated settings.
Security, governance, and compliance focus
Security, governance, and compliance will also become instrumental in the evolution of AI-Assisted Development. Enterprises will embrace AI tools that include auditability and explainable outputs, as well as more stringent data controls to meet regulatory requirements. As we look to 2026 and beyond, the measure of success for AI-assisted development will no longer solely be defined by velocity but rather by how responsibly, transparently, and security-conscious artificial intelligence is adopted into the software development life cycle.
Conclusion
AI-Assisted Development is a powerful tool in today's arsenal of software engineering, and it can fast-track you to speed, efficiency, and even code quality when used appropriately. But by embracing it, one also gets several security, compliance, IP, and long-term maintainability problems for free.
How the balance between automation and human oversight is struck will be critical to the success of AI-Assisted Development, as we move into 2026 and beyond. Organizations like Talentelgia Technologies that can ensure strong governance, foster critical thinking, and embrace AI as an enabler – not a revolution – will be most likely to succeed in developing secure, scalable, future-ready software.
Connect With Expert Developers Today!


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture














 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: