What’s the biggest challenge in software development today: speed, quality, or adaptability? The truth is, modern projects demand all three. Traditional development models, such as Waterfall, often struggle to keep pace with rapidly changing user needs and evolving market dynamics. That’s why Agile has become the go-to approach for software teams worldwide. Rooted in collaboration, rapid iterations, and continuous feedback, Agile helps deliver high-quality software that truly resonates with users. In this blog, we’ll break down elements of ‘Agile & Scrum in Software Development‘. What Agile means, explore how Scrum fits into the picture, weigh its benefits and drawbacks, and compare it with the Waterfall model—so you can confidently choose the right development methodology for your next project.
What Is Agile In Software Development?
Agile Software Development is a modern user-centric methodology that allows software to be built in a quick, flexible, and interactive process. Rather than relying on inflexible long-term roadmaps, Agile works in short, repeating cycles that deliver working software consistently, allowing a team to adapt rapidly to changing requirements and user input.
Fuelled by the Agile Manifesto, at its core, Agile is based on four value pillars;
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration vs contract negotiation
- Agile provides for responding to change rather than sticking to a certain plan
In this model, the development team and client can sit together, make decisions in real-time, select features based on an ordered list defined by user needs (not upfront), and deliver value at regular intervals. Be it any field of development, web app, enterprise software or mobile platform, Agile brings in faster releases, effective communication, and improved customer satisfaction.
Benefits Of Agile In Software Development
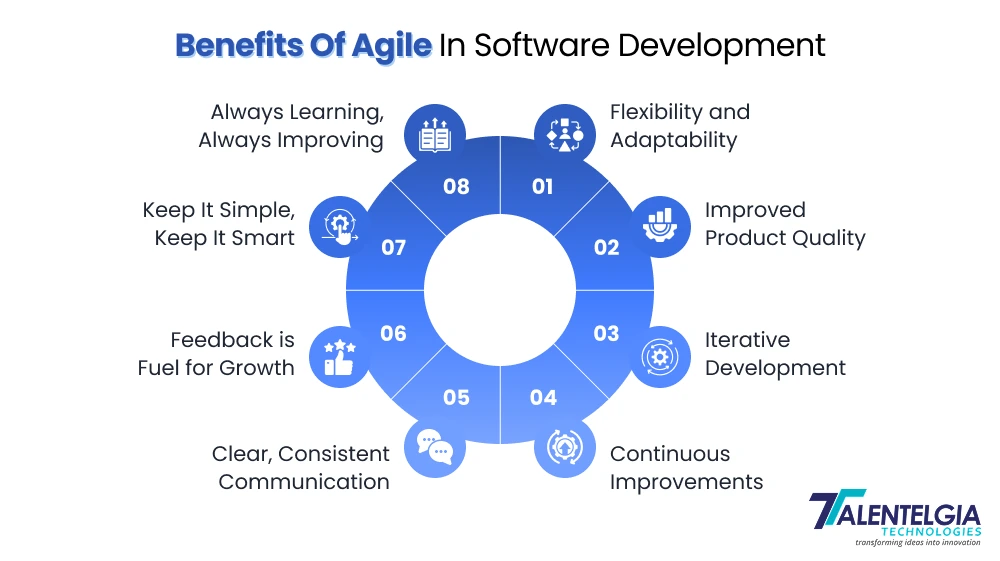
- Flexibility and Adaptability
This model shows flexibility to change at any moment of the process during its development. This is a customer-focused model and can quickly adapt to any new change based on the market. Instead, the other conventional method is not agile to alterations in stages. Agile model supports the iterative process and takes feedback iteratively to apply changes, but traditional methods as the waterfall model, have little or no hand in adopting changes. Agile is the best model in which incremental development can be achieved at every iteration of the project. It helps the team to learn from changing requirements, and the system evolves to adjust to changes.
The Agile Model stresses the continuous iteration of development and testing by members of a team. This enables the team to identify and solve problems in real time, which improves the overall quality of the system.
- Improved Product Quality
One of the central principles of Agile software development is delivering real value to the customer. Agile teams get feedback early and often, make necessary changes, and produce working software in short cycles, so the end product more closely meets the actual needs of the customer rather than what was planned at the outset.
This iterative process helps developers find problems quickly, keep the codebase of high quality, and iterate on features based on actual user feedback. So in the end, you get something that works but is also timely, relevant to users and businesses alike.
Today, customers expect more than mere working software; they are looking for reliable solutions that are user-friendly and cater to their requirements. Agile helps teams deliver on these expectations, which then leads to trust and longer-term satisfaction. This long-term customer-centric focus is a true gift for any software business as it ensures repeat business, positive referrals, and longevity.
- Iterative Development
One of the fundamental principles of Agile is that it takes an iterative approach to software development, whereby the project evolves through the process of repeated cycles (iterations or sprints), rather than going through a single cycle once. The point of each iteration is to build a piece of the software that works, so they can test it, then gather feedback and adjust until they have a complete usable product.
This method splits up large, complicated requirements into small, complete units that new features can be built and deployed as soon as they are ready, and allows for faster response to user feedback. All those incremental builds accumulate and sum up to a complete solution as close to the quality expected by the customer
- Continuous Improvements
Agile is not only about delivering faster, but it also brings the power of better evolution. Continuous improvement: One of the central tenets of agile is its continuous improvement; in every iteration, there is review and learning. Instead of saving spotting errors till the end build, in Agile teams, test and review ongoingly what is working and what’s not, changing small actionable items will bring big changes.
It helps avoid the negative surprise phenomenon (such as last-minute surprises or big bugs) and, more importantly, it keeps the product connected to the needs of those out there using your service. From a performance tweak to a UI update or even shifting priorities, Agile encourages development feedback loops and adapting proactively. The result? A product that not only meets, but consistently increases the quality of your expectations — and that is exactly what users want.
Disadvantages Of Agile In Software Development
While Agile offers flexibility and faster delivery, it’s not without its drawbacks. This guide uncovers the common challenges, pitfalls, and limitations teams encounter when implementing Agile in software development with these points:
- Clear, Consistent Communication
You cannot complete Agile software development without open and continuous communication. To that, the single source of truth also prevents delays in future testing, errors during deployment, or the need for making assumptions by providing a central place where everyone, including developers, testers, and stakeholders, can figure out what is going on. In Agile testing, collaboration is a must, and there should be feedback loops open at each stage of software development.
- Feedback is Fuel for Growth
Let’s be real, any developer is proud of their work. Agile testing, however, emphasizes a positive feedback loop through in-the-moment critique. Why? After all, it is not about getting to perfection, it is progress. They are open to feedback; every suggestion makes the product closer to adding real user value, and agile testers respect it.
- Keep It Simple, Keep It Smart
Agile testers don’t overcomplicate things. They do not run infinite test cases to solve everything. The idea is an easy one: value does not come from doing — it comes from done, and when you do what matters most. Agile team trim test suite and make sure only necessary tests are running during the Agile process, so not only do they get quickly executed, but also it saves time of QA for failing of this test.
- Always Learning, Always Improving
Agile testing is not a one-shot case, but it’s a learning process. Testers are continuously analyzing results, taking feedback, and tweaking their methods. Agile culture is all about continuous improvement, whether we make changes in our testing strategy or utilize smarter tools.
What Is Scrum in Software Development?
Scrum is a method for managing development projects in agile, collaborative processes. Scrum tools and techniques are utilized to encourage teams to work together at their best despite changes and complexities that need to be accounted for on a rolling basis. It guides teams to plan, build, and deliver work incrementally (sprints). Scrum allows teams to adapt and focus on creating valuable products by promoting constant feedback, improvement, and transparency. Icebreaking is a creative and adaptive capability; it is an iterative process that makes sure that the outcome produced resonates with user requirements and business objectives.
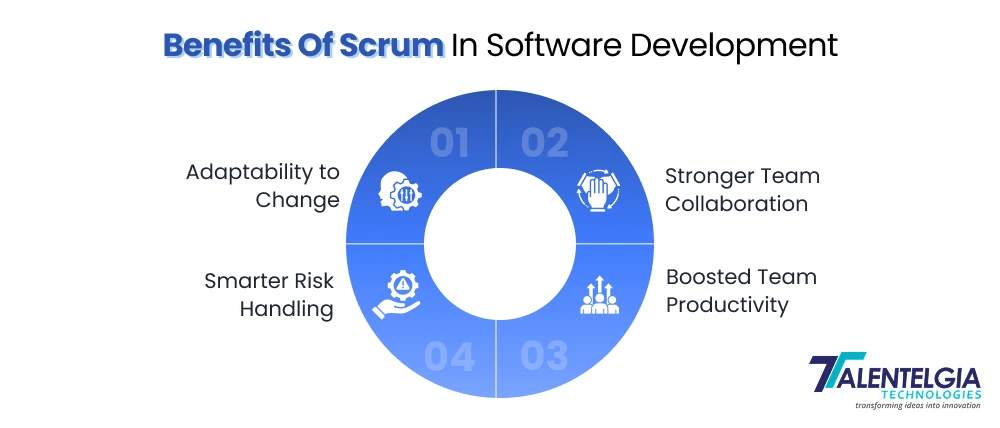
Benefits Of Scrum In Software Development
Scrum is more than just a framework; it is a mindset change to increase effectiveness, efficiency, and collaboration within teams. When done right, this can greatly improve both the product and the people running it.
Some of the main advantages that make Scrum a popular choice amongst modern software teams are:
- Adaptability to Change
The sprint-based workflow of Scrum enables teams to revise priorities frequently. They plan every 1–4 weeks to see what is working and what needs to change, adjust accordingly.
Product Owners prep with developers to groom and refactor the backlog before every sprint. This has the team working on whatever delivers the most impact and value first (regardless of when it was added to the list.
- Stronger Team Collaboration
It helps to create a very collaborative space where everyone owns everything and communication is open in the team. Its distinct roles, events, and commitments ensure every stakeholder remains aligned and accountable.
In Scrum, team members are all-rounders; most of them can perform different types of work. And when something more complicated appears on the horizon, developers get together and do a brainstorm, and they will design and solve the problems. This leads, not only to better solutions but also, with the right tools, to making things get done much quicker than while working in silos.
- Boosted Team Productivity
Once you trust the teams to manage their work, magic happens. Developers in a Scrum team don’t get assigned tasks; they agree with each other based on their strengths and bandwidth. And this self-organization gives a sense of ownership and keeps everyone focused.
Scrum empowers the developers to solve their problems instead of being micro-managed, and it is built on a foundation of shared values such as openness, respect, courage, and commitment. Everyone is working towards the same goal; they are all supporting each other and being honest with one another about what roadblocks are in their way. The result? Faster, better work is produced.
- Smarter Risk Handling
There is risk management carried through the whole course of software making, made up basic of bits interlaced into the development cadence and not a single one-off itemized balancing question. By breaking work down into small, bite-sized pieces and the continuous feedback of relending stakeholders, risks are identified faster and managed before they become bigger issues.
Developers are primed to stay on alert for possible issues as they work, so risk is less of an afterthought and more of a consideration while building. Such inbuilt awareness results in fewer surprises and continued success, sprint after sprint.
Disadvantages Of Scrum In Software Development
Scrum can boost collaboration and productivity, but it’s not a perfect fit for every project. Here, we explore the key challenges, limitations, and potential drawbacks of using Scrum in software development with these points:
1. Risk of Scope Creep
Scrum is flexible by design—it’s built to accommodate change. But without clear boundaries, this flexibility can sometimes lead to uncontrolled changes or additions to the project, commonly known as scope creep. Since Scrum works in short sprints and encourages continuous feedback, new features and ideas often pop up mid-way. While that can be great for innovation, it can also blur the vision, extend timelines, and affect the overall stability of the product—especially if a project doesn’t have a well-defined end goal.
2. High Dependency on Team Commitment
Scrum is about teamwork and responsibility. When you’ve even just one member not completely engaging or buying into the process, that will create a ripple down the sprint line. Scrum leaves no room for passive developers, testers or designers ,and every member is ingrained with the idea of proactively taking ownership to contribute their best version. The result is that momentum slows, disputes erupt and progress grinds to a halt in unmotivated teams.
3. Not Ideal for Larger Teams
Scrum is proven to work well with a small cross-functional team (preferably 5–9 members). With the size of the team, communication is becoming more complicated, decision-making becomes slow and lengthy stand-ups turn any day into a meeting endlessly. It will be possible to manage a large staff in the framework of scrum, but without its division into separate, focused teams, it turns out not to use all the necessary framework tools.
4. Requires Experienced Professionals
It assumes that you already know how to write code or test software or design interfaces, and so on of the life cycle development. If your team is experienced or is new to agile practices, they may at a loss in terms of self-organization and discipline, which are expected from Scrum. Since there is no micromanagement in Scrum, the team members are expected to have proper skills to manage their time, prioritize tasks, and handle major decisions on their own. Assuming that you do not have the right knowledge to begin with & an agile mindset, Scrum would only create more confusion and blur your thoughts.
Difference Between Agile & Scrum Framework
It is important to have an insight into how various frameworks work when you decide to select a project management methodology. Agile, Scrum, and Waterfall offer different approaches based on a variety of team dynamics, project focus and delivery time period.
Everything comparing these 3 methods together can be seen side by side here.
| Aspect | Agile | Scrum | Waterfall |
| Definition | A set of values & principles for iterative development | A specific Agile framework with defined roles/events | A linear, sequential project management model |
| Approach | Iterative & incremental | Iterative, time-boxed sprints | Linear & structured |
| Structure | Flexible and adaptive | Follows fixed Scrum roles, events, and artifacts | Phased: Requirements → Design → Build → Test → Deploy |
| Team Roles | Varies based on framework | Product Owner, Scrum Master, Developers | Project Manager, Developers, Testers |
| Documentation | Light, evolving | Minimal, just enough for clarity | Heavy upfront documentation |
| Change Management | Embraces changes even late in development | Changes can be accommodated in future sprints | Difficult once the project moves past planning |
| Project Size Suitability | Medium to large, dynamic teams | Small, cross-functional teams (5–9 members ideal) | Works best for small, fixed-scope projects |
| Delivery Timeline | Continuous delivery in iterations | Delivery in 1–4 week sprints | Delivery at the end of project |
| Customer Involvement | High | Very high (Product Owner represents the user/customer) | Low (customer feedback typically at the end) |
| Risk Management | Handled incrementally with frequent reviews | Built-in via sprint reviews and retrospectives | Addressed mainly in planning and testing phases |
| Examples of Use | software development for startups, product companies, evolving requirements | SaaS development, product design, mobile app iterations | Addressed mainly in the planning and testing phases |
Conclusion
Understanding Agile & Scrum in Software Development is essential for selecting the right approach tailored to your project's needs, team structure, and delivery goals. While Agile offers flexibility, continuous feedback, and adaptability across various development environments, Scrum takes it a step further with clearly defined roles, sprint planning, and team empowerment—ideal for small, cross-functional teams. Each methodology has its strengths and limitations, and the right choice depends on factors like team size, experience, complexity, and the need for adaptability or predictability.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: