Inference is one of the significant aspects in AI because it enables understanding of information, prediction, and solution-finding, from applications like ‘Grammarly’, which checks your grammar, to fully autonomous vehicles that drive themselves. AI uses inference to understand the world by identifying patterns in the provided data. Generative AI Development, including “ChatGPT”, requires using AI inference. This is the process by which AI systems mimic thinking, logical reasoning, and respond to queries.
The process begins with an AI model being trained on a sufficiently large set of data for the model to make predictions and decisions. Inside every AI model, there are decision-making algorithms interfaced with a neural network with the structure of a large language model (LLM). For instance, an AI model was created for a particular task, such as facial recognition. This model could be trained with a data set of millions of human faces.
Ultimately, the model successfully detects and recognizes individual faces, and retains distinctive features like eye shape and colour, nose shape and hair colour, as well as using these features to identify any individual in a given image. In this article, we examine the specifics of inference in AI, its importance, and ways to implement it, actual applications, and the continuing intelligent systems to construct a pathway.
Understanding AI Inference: Types, Components & Working Process
Core Definition:
AI inference is the process by which a trained Artificial Intelligence (AI) model makes predictions or decisions based on new, unseen data. It’s effectively the “execution phase” where the AI model, having already learned patterns during training, is applied to real-world inputs to generate thoughtful outputs instantly. Unlike training, which involves feeding vast datasets to teach the model from scratch and demands extensive computational resources, inference focuses on leveraging this knowledge in a timely, efficient manner.
For instance, in an AI voice assistant, AI inference allows the system to understand a user’s spoken request, identify the intent, and respond appropriately in real time. This happens thousands of times per second in modern applications like image recognition, fraud detection, and language translation, showcasing how inference underpins the practical use of AI technologies.
Types of AI Inference
What is more useful in an AI system: The capability to make near-real-time decisions with high accuracy, such as identifying potential fraud in large transactions, or the ability to predict future events from the available data, like a sensor programmed to request maintenance before a failure occurs? Knowing the differences among various AI inference approaches should help in determining the optimal model for your application.
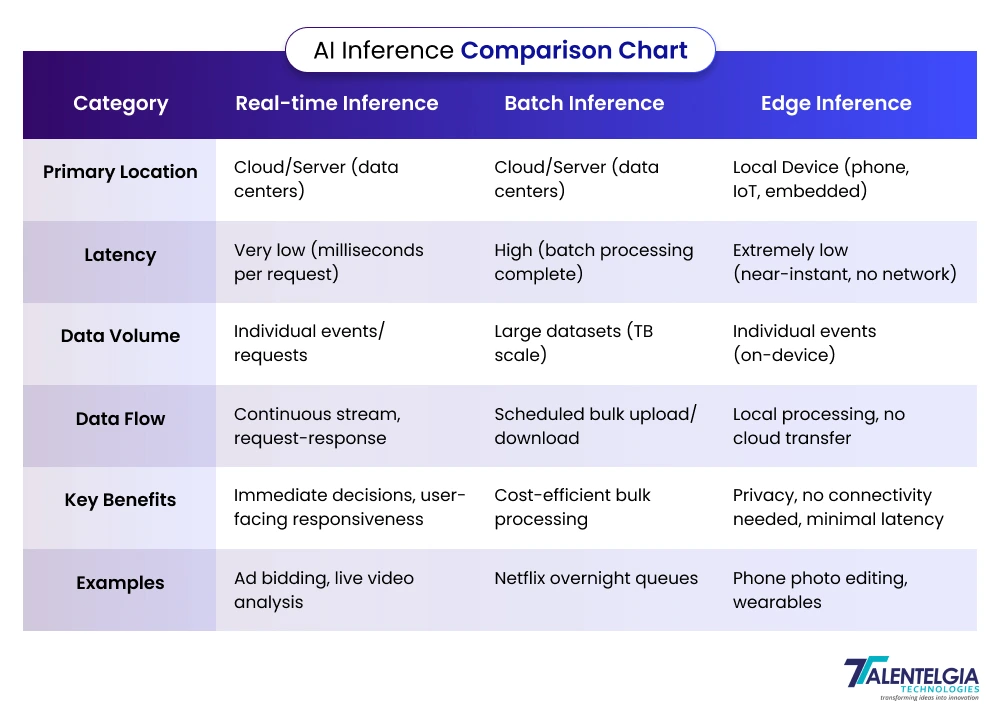
- Cloud Inference (Power & Scale)
As mentioned, inference is performed using powerful, distant remote servers in a data center, which is the most common approach. The cloud is beneficial in this case because it is very scalable and can accommodate complex datasets and models. There are usually two main types of inference done in the cloud:
- Real-time (online) inference: this is important for interactive applications where instant responses are crucial, as it facilitates the processing of incoming requests in milliseconds, sometimes even microseconds.
- Batch (offline) inference: This type of inference processes large amounts of data at once and is useful when immediate answers are not needed. It is very cost-efficient for analyses and tasks performed at regular intervals.
Read More: How Much Does It Cost to Train an AI Model?
- Edge Inference (Speed & Privacy)
Inference is performed on the device where data is created, which can be a smartphone or an industrial sensor. They are directly run on local devices (smartphones, IoT) to reduce reliance on cloud connectivity and improve privacy.
Technical Components of AI Inference
AI inference relies on a sophisticated stack of software engines, hardware accelerators, and optimization techniques working in harmony to deliver predictions at scale. Understanding these components reveals why inference powers everything from real-time fraud detection to on-device smartphone AI—balancing speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
General-purpose processors excel at sequential tasks like data preprocessing, orchestration, and lightweight inference. ARM CPUs power edge devices with low power (5-85W), while x86 server CPUs (Intel Xeon, AMD EPYC) coordinate GPU clusters. Weakest parallel performance but universal compatibility.
2. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Parallel compute kings (NVIDIA H100/A100, AMD MI300) dominate matrix-heavy neural net operations, delivering 100+ tokens/second for LLMs. 200-400W power draw enables training+high-volume inference but requires cooling. The CUDA/TensorRT ecosystem is mature.
3. Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)
Reconfigurable accelerators (Xilinx Versal, Intel Agilex) offer custom pipelines for low-latency edge AI, blending GPU speed with ASIC efficiency. High development time, but reprogrammable for algorithm updates. Power: 50-200W, ideal prototyping.
4. Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC)
Fixed-function champions (Google TPU v5, Apple Neural Engine) achieve peak efficiency post-design, crushing inference/Watt ratios. NRE costs $1M+ and 1-2 year timelines limit volume production. Unmatched for dedicated AI chips.
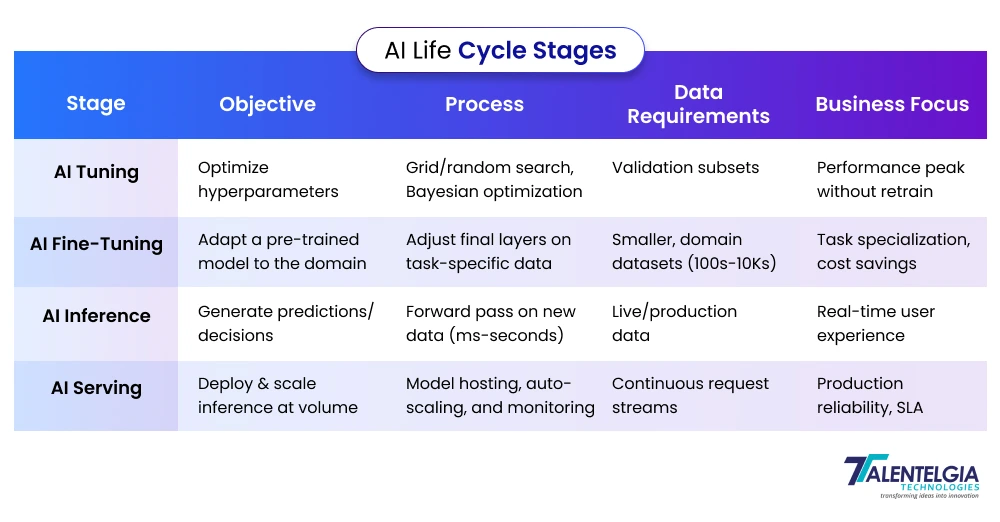
AI Inference vs. Training vs. Machine Learning: Key Differences
Although the entire AI life cycle encompasses everything from collecting data to monitoring it in the long term, the life cycle of the AI model itself travels from inception to deployment in three key stages. The first two are about acquiring knowledge, and the last one is about applying that knowledge. Understanding the distinctions between AI training, inference, and machine learning is crucial for optimizing AI workflows.
- Machine Learning: Machine Learning is the overall discipline involving algorithms that learn from data to enable AI systems to recognize patterns, make predictions, or classify information without explicit programming. It’s the foundation that powers AI capabilities.
- Training: is the process within machine learning where a model is fed vast amounts of curated data to learn the relationships and rules within it. This is computationally intensive and can take from hours to weeks, as it adjusts model parameters to improve accuracy and generalization to unseen data.
- AI Inference: is the stage where a trained model applies its learned knowledge to new, unseen inputs to generate predictions or decisions. It requires less compute power and is optimized for speed and efficiency since it delivers live results in applications like voice assistants and fraud detection.
How Does AI Inference Work?
AI inference is the process by which a trained machine learning model applies its learned knowledge to new, unseen data to produce predictions, classifications, or decisions. This is the stage that brings AI to life in real-world applications like voice assistants, image recognition, and fraud detection.
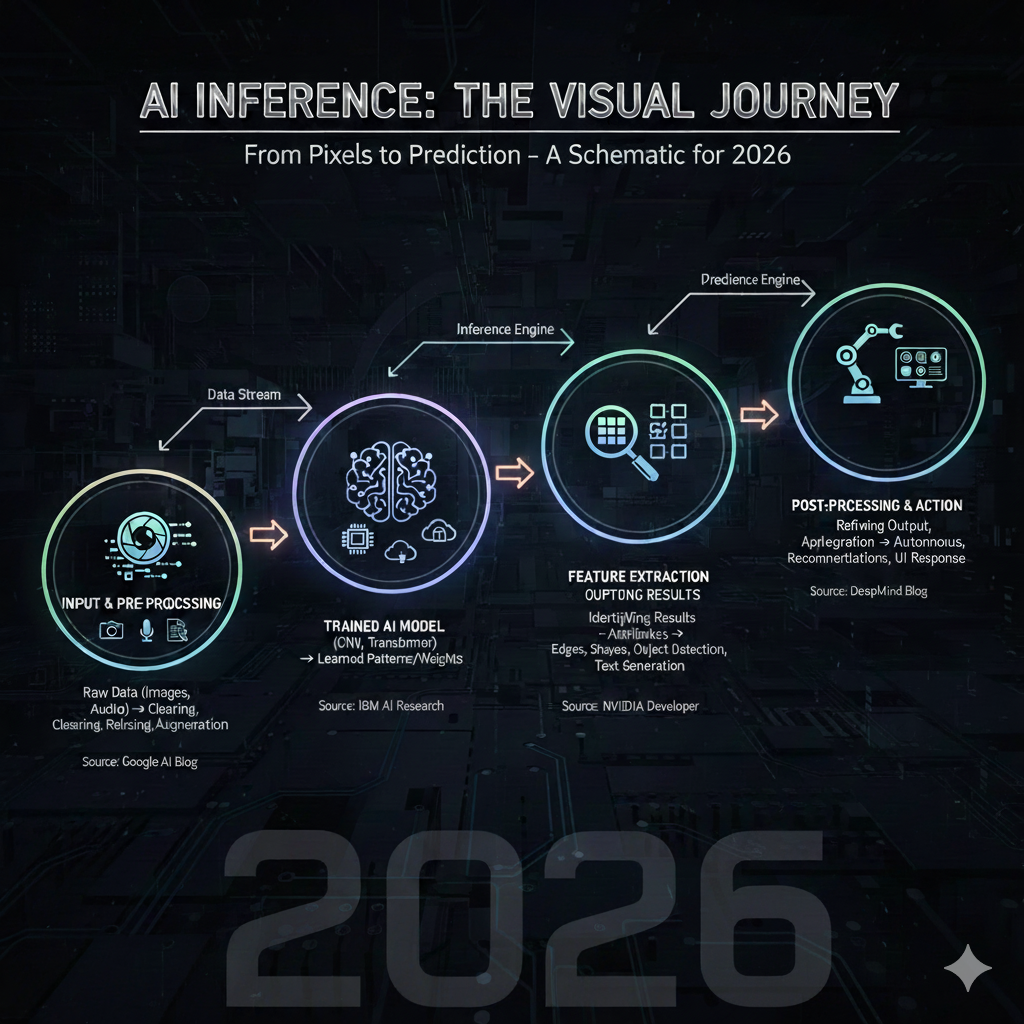
Here’s a simplified flow of AI inference:
- Data Preparation: Incoming input—such as text, images, or sensor data—is preprocessed to fit the model’s expected format. This may involve normalization, resizing, or tokenization to make the data machine-readable.
- Model Execution: The preprocessed input is passed through the neural network layers of the trained model. The model applies learned parameters (weights and biases) to analyze patterns and calculate probable outcomes.
- Prediction Generation: The model produces an output—this might be a label, score, or specific action—representing its best guess based on prior training.
- Output Processing: The raw prediction is then translated into user-actionable results, such as showing translated text, recognizing faces in photos, or approving a transaction.
This entire sequence typically runs in milliseconds, supported by optimized hardware and software stacks designed to minimize latency and maintain accuracy. Efficient inference is what enables real-time AI interactions that feel seamless and intelligent.
Why Is AI Inference Important?
AI inference isn’t just technical plumbing—it’s the profit engine turning AI experiments into revenue machines. Here’s why smart companies obsess over inference excellence.
- Instant Decision-Making That Feels Magical
AI inference powers lightning-fast responses—transforming how users experience smart assistants, fraud detection systems, and autonomous tech. Immediate predictions elevate customer interactions and safety.
- Cost Efficiency
Running inference consumes far fewer computing resources than training, making it possible to embed AI broadly while managing operational expenses intelligently.
- Enhanced Privacy and Security
On-device inference limits data exposure by keeping sensitive information local, safeguarding user privacy, and aligning with stringent regulatory requirements in finance, healthcare, and beyond.
- Offline Readiness for Any Environment
Edge inference empowers devices to act independently of cloud connectivity, enabling seamless, reliable AI functionality in remote or bandwidth-stretched settings.
- Unmatched Scalability for Enterprise Impact
AI inference architectures handle surges effortlessly—from scaling recommendation engines to supporting massive user bases—without compromising quality or speed.
- Catalyst for Edge AI Revolution
As billions of connected devices demand real-time intelligence, inference drives AI’s shift from centralized clouds to pervasive, smart hardware around us.
- Competitive Advantage Through Latency
Superior AI responsiveness differentiates brands, as subtle latency improvements can increase customer retention, engagement, and revenue significantly.
- Eco-Friendly AI Deployment
Optimized inference reduces power consumption of AI workloads, supporting sustainability goals while maintaining high performance.
Real World Applications of AI Inference
AI inference powers many vital real-world applications by turning trained models into instant decision-makers.
1. Large Language Models (LLMs):
Quickly generating human-like text for chatbots, content creation, and virtual assistants, making interactions seamless and natural.
2. Predictive Analytics:
Analyzing data trends instantly to forecast outcomes in marketing, sales, and operations, enabling proactive business decisions.
3. Email Security:
Scanning messages as threat detection in real time to detect phishing, malware, and spam, protecting users and enterprises from evolving cyber threats.
4. Finance and Fraud Detection:
Banks use AI to analyze transactions in milliseconds, blocking fraud and assessing credit risks in real time.
5. E-commerce Personalization:
Retailers provide dynamic recommendations and personalized pricing by analyzing user behavior on the fly.
6. Healthcare:
AI processes medical images quickly to detect abnormalities, aiding faster diagnoses and triage.
Read More: How AI is Enhancing Early Disease Detection Through …
7. Autonomous Vehicles:
Self-driving cars utilize edge inference to interpret sensor data instantly, ensuring safe navigation.
8. Industrial Automation:
Factories monitor equipment health and product quality in real time to prevent downtime and defects.
9. Edge AI Devices:
Smart cameras and wearables perform on-device detection and monitoring, enhancing security and health tracking without cloud dependency.
The Future of AI Inference
AI Inference will soon be able to operate from local machines instead of being confined to massive data centers. Even while deep learning AIs continue to operate on data from centralized hubs, advancements in prediction analytics devices and data processing at the source will eventually move “last mile” AI technologies to smaller devices.
In the future, robots will be able to detect and track faces, objects, and analyze human behavior and make decisions autonomously with the help of machine learning and computer vision technologies. Recently, people have publicly spoken about these technologies as a foundation for “general-purpose robots”. In the upcoming years, numerous such devices will rely on “inference at the edge” technology.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture













 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: