In general, businesses can be perceived as complex puzzles, where every piece represents a separate department. For business managers to acquire a certain perspective, every piece, such as sales, marketing, manufacturing, finance, customer service, and human resources, must fit together perfectly. With that in mind, ERP Development are one of the most specialised methods for establishing seamless connections, often natively incorporating all these pieces, plus additional ones, into a consolidated database that enables business processes, workflows, and insights to be unified.
Moreover, ERP integrations are an ideal means for the future, extending the efficiency and productivity benefits of ERP system integration to additional applications, whether those are independent applications or homegrown proprietary solutions, through ERP software integrations. Integrations can be tricky, however. Linking various systems together, such as in the case of some multi-system setups, can lead to a degree of interdependence that results in a chain reaction if one system fails. Thus, understanding their Do’s and Don’ts and how to implement them can help companies understand their landscape.
Understanding ERP Integration: An Overview
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are the backbone of modern business, integrating core functions like finance, HR, supply chain, and sales into a unified platform. ERP integration connects this central platform with other critical business applications CRM, eCommerce, or payroll, creating seamless data flows and automating processes for greater accuracy and efficiency.
All types of companies from various industries have begun to adopt ERP software. Some of the key benefits of ERP integration are:
- Operational efficiency: Decreases time from administrative processes in responding to queries, streamlining business operations across systems, automating processes, eliminating manual data entry, and creating datasets.
- Data Accuracy: Provides a singular, synchronized, and cohesive unified data across systems and data sources to ensure there are no discrepancies and to retain data integrity in systems.
- Reporting & Analytics: Enhances and streamlines operational data and reports from analytics by standardizing processes to cut costs, combining with other processes, and by single-entry consolidation of data.
- Adaptability: Assists in business continuity and operational flexibility in the organization by being disruption-free with no major operational changes, even when there are technology mergers, acquisitions, divestitures, or changes.
- Service Delivery: Improves response time and provides more accessible data to customer service representatives by integrating the transactional back-office system with the customer-facing system to offer tailored and more active services.
- Supply Chain Integration: Supports supply chain operations by integrating and interconnecting the ERP to available supplier portal systems, user transportation systems, and warehousing operations, such as providing.
How Does ERP Integration Work?
ERP integration functions by creating communication pathways and data exchange frameworks between the ERP system and other software applications. This involves linking the ERP’s
application programming interfaces (APIs) with those of external systems to facilitate smooth and uninterrupted data transfer.
Technically, this integration often depends on middleware or integration platforms that act as bridges between the ERP and other applications. These middleware tools handle data format translations and transformations, ensuring that information remains compatible and consistent across different systems.
A vital part of the process is aligning data fields between the ERP and the connected applications. This mapping guarantees that data is properly synchronized and accurately matched, preventing issues like duplication or misinterpretation.
Once successfully connected, the systems can exchange data in both directions, enabling real-time updates and seamless information sharing. This integration supports core business areas such as finance, sales, inventory, and HR by providing timely access to precise and current data from multiple sources.
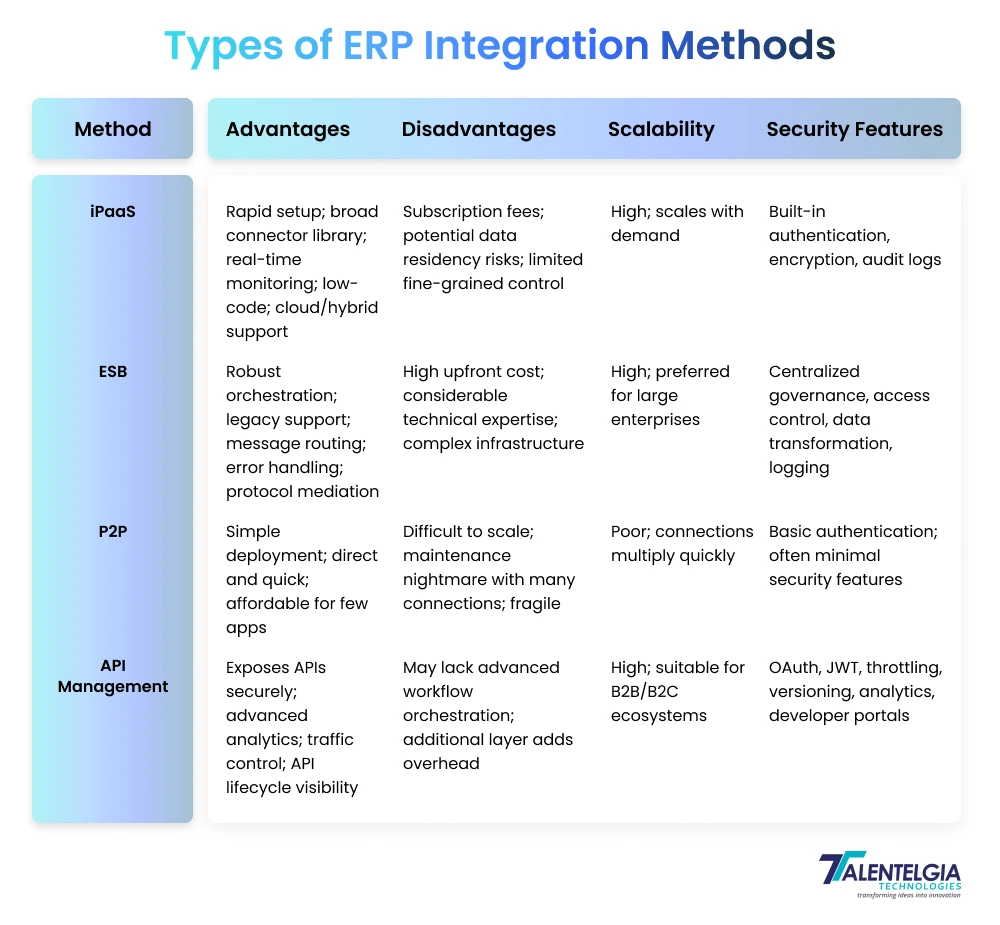
Major ERP Integration Methods of Managing APIs
The enterprise resource planning integration landscape is multifaceted. There are over 800 different free open-source API management tools to advanced iPaaS products. More primitive approaches include point-to-point (P2P) and enterprise service bus (ESB) models, of which some companies are still reliant upon. However, the industry standard is now cloud-hosted, scalable, iPaaS integration solutions.

The following outlines some of the more popular methods of ERP integration – their advantages and disadvantages.
1. iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
iPaaS is a cloud-native platform that connects applications through pre-built connectors, low-code workflow tools, and automated scaling. It handles both cloud and on-premises data sources, making it ideal for businesses seeking rapid implementation and minimal technical overhead. iPaaS manages data mapping, transformation, and orchestration out-of-the-box while providing real-time monitoring, error handling, and integration lifecycle management. Popular examples: Boomi, MuleSoft, Zapier.
2. ESB (Enterprise Service Bus)
ESB acts as a centralised middleware layer, connecting legacy and modern applications while handling message routing, data transformation, protocol mediation, and security. ESBs decouple applications, allowing flexible and reusable integration without modifying individual endpoints. ESB is preferred for complex multi-system architectures requiring robust orchestration of asynchronous processes and transaction management. Examples: IBM Integration Bus, TIBCO ActiveMatrix.
3. Point-to-Point (P2P) Integration
P2P integration directly connects two applications using native plugins or custom API code. While simple and cost-effective for limited scenarios, P2P becomes challenging as the number of connections grows, leading to tangled networks and maintenance headaches. Still, it works well for small teams or single-purpose integrations with clear relationships.
4. API-Based Management
API Management platforms govern published APIs, ensuring secure, scalable, and monitored access. They power both internal and external connectivity, enable partner integrations, and manage lifecycle operations like authentication, rate limiting, analytics, and versioning. API-based management excels at exposing data reliably to mobile, web, or third-party developer ecosystems—examples include Apigee, Azure API Management, and Kong.
Read More: Which ERP System is Best
Typical Use Cases of ERP Software Integration
There are as many ERP integration methods as there are types available. Some ERP systems offer comprehensive integrations with other applications to automate data transfers and process integrations across the different modules. However, companies sometimes prefer third-party applications, including custom software for the relevant ones, due to better familiarity and desirable functionality. Below are the most common ERP integrations.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Integration
Imagine a sales team with instant access to real-time customer data—orders, preferences, support tickets—without switching between systems. CRM and ERP integration creates a unified view of customer interactions, enabling personalised service and proactive engagement. For instance, when a customer service query arises, agents can immediately see order history, delivery status, and payment details, leading to faster resolution and enhanced loyalty.
- eCommerce Platform Integration
Envision a company selling online and in stores, having synchronised stock levels across all channels. When ERP integrates with eCommerce platforms like Shopify or Magento, product availability, pricing, and promotions update automatically. This eliminates overselling, reduces stockouts, and provides customers with accurate, instant information—transforming the shopping experience into a hassle-free, omnichannel journey.
- Customer Service Software Integration
Customer support is more impactful when service tickets, product data, and order history are interconnected. Integration ensures support agents have complete visibility—tracking an issue from complaint to resolution—without manual data entry. This results in faster, more accurate responses, and builds trust as customers feel valued and understood.
- Accounts Payable (AP) Automation Software Integration
Imagine eliminating manual invoice entry and speeding up approvals. When ERP connects with AP automation tools, incoming invoices are automatically matched with purchase orders, dates, and vendor data. Payments are scheduled in real time, reducing delays and errors, and freeing finance teams to focus on strategic financial planning rather than routine work.
- Human Resources (HR) Systems Integration
HR and ERP integration transforms employee data management. It ensures that onboarding, payroll, time tracking, and benefits are consistent and accurate across platforms. For example, new hire info entered into HR systems flows seamlessly into payroll and compliance modules, minimising manual errors and speeding up onboarding.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
In manufacturing and product development, integrating ERP with PLM solutions synchronises design, engineering changes, and production schedules. This leads to faster product launches, better quality control, and cost savings, as teams collaborate more effectively across the entire product journey—from conception to market.
- Project Management Software Integration
When project timelines, budgets, and resource plans are linked to ERP data, organisations gain insight into project costs, procurement, and staffing needs. For instance, real-time inventory data linked with project management tools prevents delays due to stock shortages, enabling smarter planning and timely delivery.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Software Integration
Integrating ERP with BI tools like Power BI or Tableau aggregates data across functions, creating dynamic dashboards and predictive reports. Imagine management making strategic decisions based on real-time sales trends, supply chain performance, and customer feedback—driving growth with confidence.
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
EDI automates the exchange of purchase orders, invoices, and shipment notices with suppliers and logistics partners. This reduces manual entry, accelerates transaction cycles, and enhances supply chain transparency—crucial in industries like retail and manufacturing with high transaction volumes.
- Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
ERP integration with EAM solutions enables organisations to monitor, maintain, and optimise their physical assets. For example, real-time data on machinery health informs predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and extending asset life—a vital component in manufacturing, utilities, and transportation sectors.
Also Read: Benefits of ERP Inventory Management System
Conclusion
If there is one thing to understand about ERP integration across a business, it is about appearing in perfect balance. Each business has its needs, problems, issues, and challenges. But successful ERP software integrations continue to follow a similar path, and it is the companies that estimate needs, build strong teams, and construct visions, communicating these visions to involve all stakeholders—while also justifying the cost of implementing an ERP system that create a true masterpiece.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture
















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: