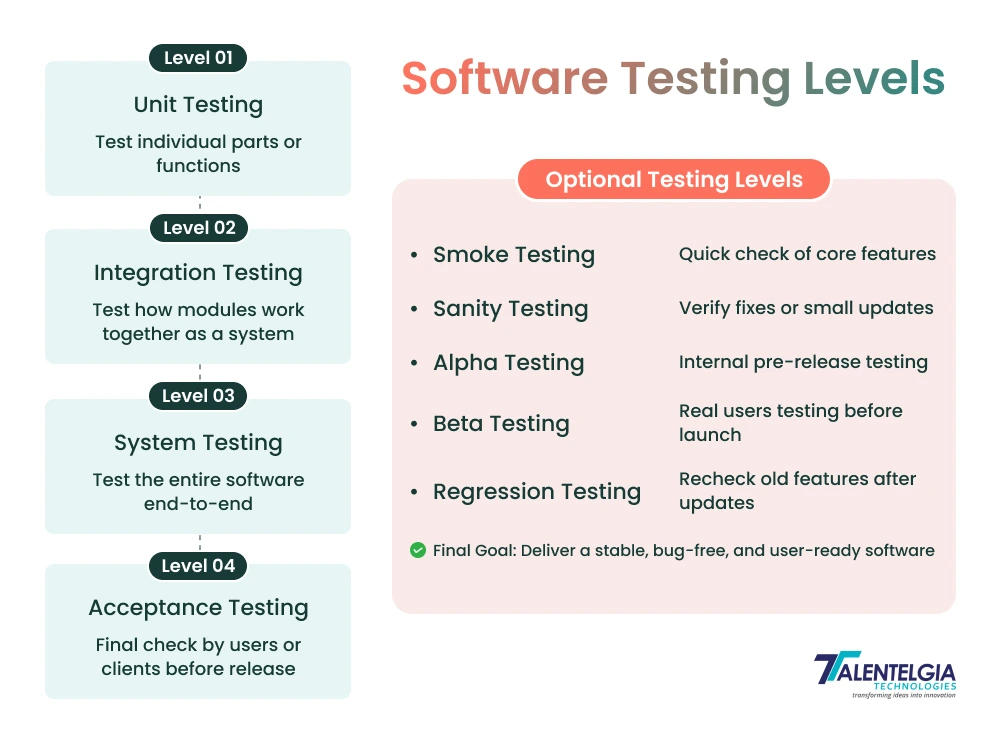
Software testing is carried out at various levels to ensure that each part of the software functions to give the outcome as expected. Software testing Levels are targeting the planned goal, which is from inspecting little pieces of code to evaluating the entire system. The main question that comes to mind is ‘What are the different Levels of Software Testing?’. The four layers are Unit Testing, Integration Testing, System Testing, and Acceptance Testing.
In most projects, teams use both automation testing service and manual testing service to support these levels. While automation helps speed up repeated checks, manual testing adds the human touch needed to catch real-world issues. Together, they make sure each level of testing is done smoothly and the software is truly ready for users.
1. Unit Testing
Unit testing is the type of software testing where individual components or parts of a software are tested. The primary objective is to verify the functionality of individual pieces of code. Developers typically do that.
Example: Testing if the login method accepts a valid username and password.
2. Integration Testing
Integration Testing Integration testing is the level of software testing where individual units are combined and tested as a group. It makes it easier to detect problems in how different parts of the system communicate or share data.
Example: Testing whether the login page is linked to the database properly.
3. System Testing
System Test: System testing is a software testing level where you test the entire application. The aim is to ensure that the entire system conforms to all the specifications and performs well in practical situations.
For example: Testing an e-commerce website end-to-end from product search to payment.
4. Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing is the level of software testing in which a system is tested for acceptability. The idea is to confirm that the software fulfills business requirements and is prepared to be launched live.
For Example, A customer sees if they can place, and then easily track orders through an online shop.
Also Read: Differences Between Black Box Testing and White …
Some Optional Levels of Software Testing
While the main levels of software testing ensure that the core structure of the software is solid, there are also several optional testing levels that add an extra layer of quality and reliability. These tests are not always mandatory, but they help teams catch hidden issues early, validate recent changes, and understand how real users interact with the system. Optional testing levels like Smoke, Sanity, Alpha, Beta, and Regression Testing make the software more stable and dependable before it reaches end users.
Smoke Testing
Smoke testing is the testing which usually run on the major features of a piece of software to ensure that everything is working. It also makes sure the fundamental functions do what they should before deeper testing takes place.
Example: Is the app open and its main pages loaded?
Sanity Testing
The degree of software testing performed to assess a new patch or bug fix. It also makes sure recent updates didn’t break other parts of the software.
Example: After resolving an issue with logging in, testers verify that users can still log in without any issues.
Alpha Testing
Alpha software testing – it’s a level of software testing, when the internal team and some users are already using (testing) the app. It assists in locating — and fixing — errors early on.
Example: A company’s testing team runs an app version before distributing it to users.
Beta Testing
Beta testing is the level of product testing for which real users must put your software to work in real-world situations. Their feedback will be used to polish the final release.
Example: Releasing a “beta version” of an app only to a subset of users.
Regression Testing
Regression testing is a type of software testing that tests an application as many times as required for the upgrade or changes made to the system. It serves as a means of ensuring that the new code does not affect any existing features.
So, for example, testing the profile page a second time after working on a new notification feature.
Software Testing Levels Diagram
Summary
After going through the blog , we concluded that the above layers of software testing also make sure each application component functions properly and aligns with user demands. Testing starts from Unit Testing, where we test small code to assert its correctness. It transitions to Integration Testing, where the integrated elements are tested together. Next up is System Testing, where the entire software is tested in an environment that closely mirrors the real world. Acceptance Testing is the final validation that the software functions as expected for the customer and supports business objectives.
Optional Testing Levels—from Smoke, Sanity testing to Alpha, Beta and Regression testing—provide the additional layer(s) of Quality. These serve to verify that large-scale functionality works, bugs are resolved stably, user feedback is taken into account, and new updates do not disturb existing features.
When combined, these levels of testing are allthat the software needs to be dependable for users to use.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture














 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: