Computer resources can be accessed and used through the internet or the “Cloud”. It offers several benefits like high performance, scalability, cost savings, economies of scale, and more. For several organizations, modernizing IT and data is directly linked with migrating to cloud computing services and technology.
The term “Cloud” was first introduced during the early 2000s. Back then, it had an ambiguous meaning to it, as the idea of having access to computer data from somewhere other than on-site IT infrastructure sounded nothing less than a science fiction movie. However, the reality was a definite game-changer, not just technologically, but also in the way people run businesses.
Cloud Computing: Overview of Underlying Technology
We interact with Cloud technology almost every day, whether it’s using a cloud application such as Google Gmail, streaming movies on Netflix and Amazon Prime, or playing video games hosted on a remote cloud server. With cloud computing, you can rent the amount of computational power or storage — no need to own or maintain your own physical hardware.
From small startups to well-established enterprises, Cloud computing is indispensable for businesses of all sizes, even more than on-site computing systems, due to its flexibility and scalability that the cloud offers. For businesses, cloud computing enables an organization to provide access to required data, resources, and applications for remote employees. This creates a seamless and integrated omnichannel customer engagement, and offers the massive computing power and resources to leverage revolutionary technologies like “Generative AI” and “Quantum Computing”.
What Is Cloud Computing?
In computing, “cloud” refers to a network of remote servers accessed over the Internet to store, manage, and process data—not just on your local devices. It’s the backbone behind services like Google Drive, Netflix, and Office 365, freeing you from physical hardware and enabling you to access your files from anywhere.
Companies can utilize resources without having to buy and maintain an on-site IT infrastructure. This has benefits such as flexibility concerning resources and on-demand maintenance, innovative IT resources, and cost efficiency related to infrastructure service and maintenance. For a majority of organizations, transitioning to cloud computing services closely corresponds to the advancement of IT and data.
Who Uses Cloud Computing Services?
Who uses Cloud? The simple answer is: EVERYONE! The cloud is embedded in your smartphone, automobiles, smart watches, and even popular food delivery services.
For businesses, the cloud is even more beneficial. It allows them to be flexible and scale their operations according to their needs. Companies, regardless of size or industry, implement cloud computing. It supports them in performing their routine tasks, which include software development, disaster recovery, customer applications, virtual desktops, data protection, data analytics, server virtualisation, and several other applications.
As technology evolves, many organizations are also turning to AI Cloud Solutions to take their cloud infrastructure to the next level. These intelligent solutions help businesses integrate artificial intelligence into their cloud systems, improving automation, security, and overall efficiency.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Think of cloud computing as a powerful three-piece puzzle: behind the scenes, cloud providers operate massive fleets of physical machines housed securely in sprawling data centers around the globe. These centers serve as digital hubs, running everything from simple storage to advanced apps. The second piece is the users—anyone with an internet connection—who access these resources instantly from virtually anywhere.
The internet acts as the ultimate connective tissue. Whether you’re working across continents or syncing files from your phone, the cloud bridges vast distances in seconds, uniting data, apps, and people.
- Cloud computing connects users to remote servers hosted by cloud providers in data centers worldwide.
- Users access data and applications via the internet, eliminating the need for local hardware management.
- Previously, companies maintained costly on-site data centers with hardware upgrades, space, and energy requirements.
- Cloud providers handle infrastructure provisioning, maintenance, security, and scaling behind the scenes.
- Businesses pay for cloud resources like renting a car—use what they need, and the provider handles upkeep and upgrades.
- This model offers flexibility, cost savings, and scalability on demand without worrying about technical management.
Also Read: Cloud Computing Role in Edge AI
5 Core Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Before cloud computing, companies would buy and maintain their own on-site IT infrastructure. While reducing costs was a major factor in their initial move to the cloud, many businesses discover that public, private, or hybrid cloud infrastructure can provide significant advantages.
For agile and DevOps teams, cloud-based computing makes the development process efficient and faster.
- On-demand Self Service
On-demand self-service allows users to register and provision computing resources such as servers and storage without any human involvement from the service provider.
- Broad Network Access
Broad Network Access means that capabilities can be accessed from any device, such as laptops, tablets, and mobile phones, via the internet using standard access methods.
- Resource Pooling
Resource Pooling describes the model where the provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple customers simultaneously. These resources are dynamically assigned and reallocated based on varying customer needs.
- Scalability
Rapid Elasticity (Scalability) describes a situation where resources are automatically adjusted in response to demand. This prevents resource waste during low-demand periods and ensures that there is enough resource capacity during high-demand periods.
- Measured Service (Pay-as-you-go Model)
Measured Service (Pay-as-you-go Model) means that the provider’s systems automatically control, optimize, and report resource usage. This ensures that the customer and the provider have clear records, and you only pay for resources that you consume.
Major Types of Cloud Computing Services
There are numerous options for cloud services, and you will likely use several of them simultaneously to fulfil your requirements. They all could come from a single provider, or multiple cloud service providers could be used for different functions.
There are 4 major types of cloud computing services— software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). While the definitions of these services are clear, in practice, it can be challenging to identify the boundaries between infrastructure and platform. Customers often integrate these services in complex arrangements to address their requirements.
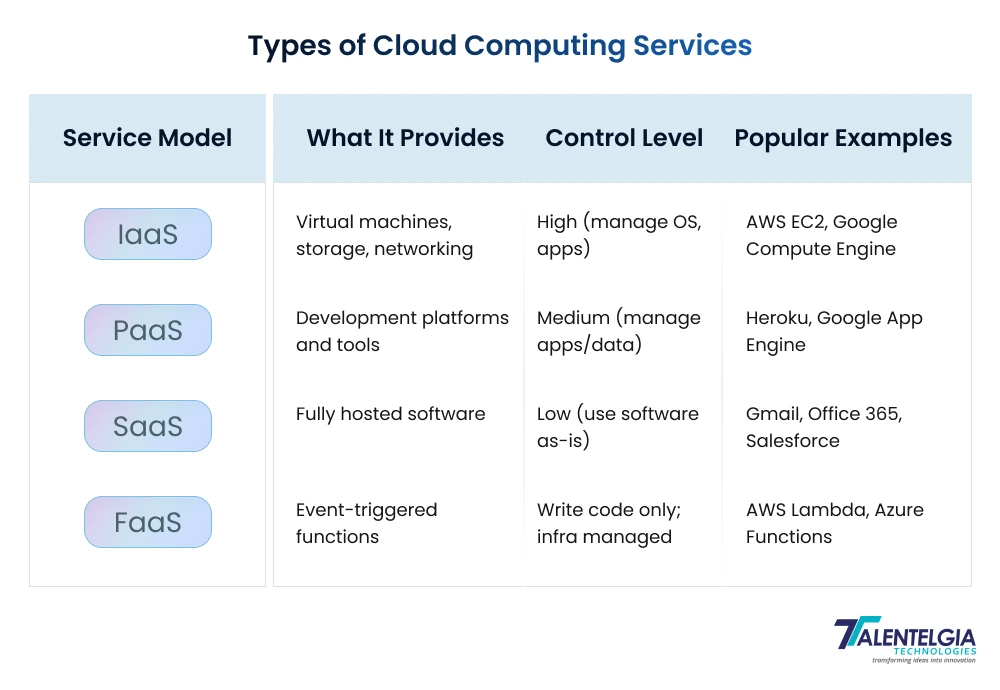
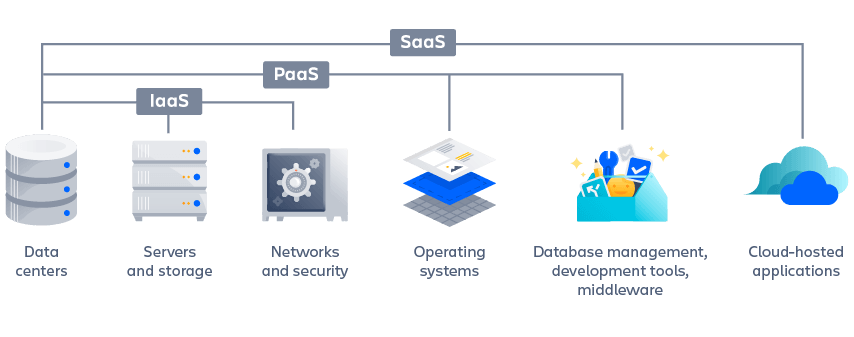
Content:
Data Centers —> Servers & Storage —> IaaS —> PaaS —> SaaS —> FaaS —>Database management, development tools, middleware —> Cloud-hosted applications
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the foundation of cloud services—imagine renting virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking over the internet. The cloud provider manages the physical hardware, data centers, and networking, while you control and customize operating systems, applications, and data. It’s like leasing a powerful computer but having freedom over how you use it. Perfect for businesses needing flexibility without hardware headaches.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is the developer’s best friend, offering a complete platform that supports building, deploying, and managing applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It provides tools like databases, development frameworks, and middleware. Picture it as a fully equipped workshop ready for developers to create software without worrying about power tools or workspace setup. It accelerates development while simplifying management.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers fully functional software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users simply log in and use the software on any device without installation or maintenance—think Gmail, Netflix, or Office 365. The provider handles everything behind the scenes, from updates to security, letting you focus on using the app without any tech stress. It’s the “plug and play” model of cloud computing.
4. Function as a Service (FaaS)
FaaS takes cloud computing one step further—it’s serverless computing in action. Instead of running entire applications continuously, you write small, independent functions triggered by events and execute them on demand. The provider manages infrastructure dynamically, charging only for execution time. This model improves efficiency, reduces costs, and accelerates development for event-driven apps.
Also Read: Cloud Computing in Banking
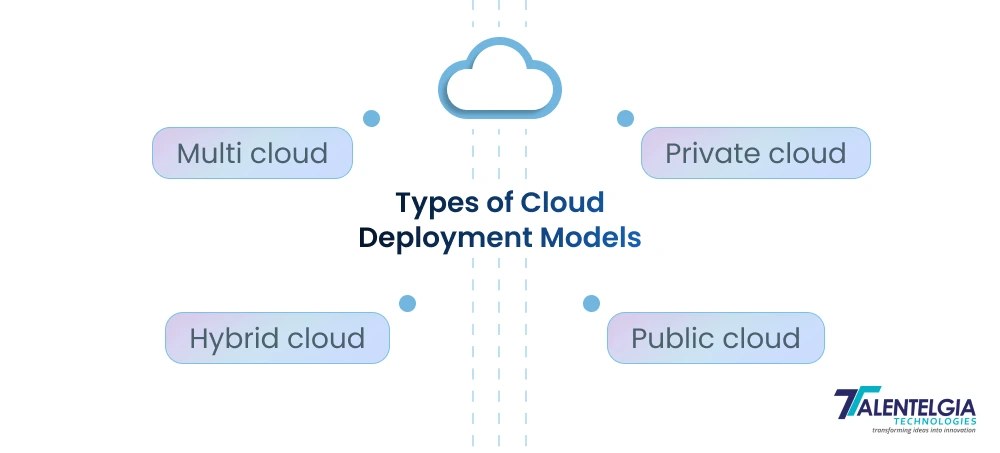
Types of Cloud Deployment Models You Must Know
All types of cloud deployment models indicate how and where your cloud solution functions. Different models provide different combinations of scalability, security, control, and collaboration, assisting organizations in establishing their ideal base in the cloud ecosystem.
- Private Cloud: This type of cloud is dedicated entirely to one organization. It may be within the organization’s off-site, off-premise, or may be managed by the organization or a third party. It delivers the greatest possible control and security.
- Public Cloud: This type of cloud infrastructure is managed by third-party providers (like AWS or Google) and is available to every subscriber over the internet. It has almost unlimited expansion potential and offers a consumption-based pricing system.
- Hybrid Cloud: A hybrid configuration combines a private cloud with one or more public clouds and facilitates the transfer of data and applications between the two. This configuration offers the highest level of flexibility because the organization can store sensitive data in a private cloud and allow other applications to access the practically limitless resources offered by the public cloud.
- Multi Cloud: This is a strategy where an organization adopts a combination of clouds and services from two or more different public cloud providers. It prevents vendor lock-in and allows the organization to utilize the best service from each vendor.
Top Leading Cloud Service Providers In 2025
In the world of cloud computing, a few of the world’s leading cloud computing providers have unique strengths and innovations with a global dominance. Picking the right cloud computing provider is like building a dream team because the decision will affect the performance, cost, security, and creativity of the cloud solutions.

Benefits of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing brings a game-changing set of benefits that have transformed how businesses operate, innovate, and compete in today’s digital arena. Here’s why cloud computing is the MVP of modern IT:
- Cost Efficiency: Say goodbye to hefty upfront investments in physical servers, maintenance, and energy costs. Cloud computing allows you to pay only for what you use, turning capital expenses into manageable operating costs. This means more budget for innovation and growth.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Business needs can change on a dime. Cloud platforms let you scale resources up or down instantly to handle traffic spikes, seasonal demands, or expansion—no hardware upgrades or delays needed. Flexibility is built right in.
- Speed and Agility: Deploy new applications, environments, and services in minutes, not weeks. This rapid provisioning boosts innovation, accelerates time-to-market, and fuels competitive advantage.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Teams spread across cities, countries, or continents can work together seamlessly in the cloud. Real-time access to files and apps improves productivity and communication, no matter where they are.
- Robust Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security protocols, data encryption, and compliance certifications. These protections shield your data better than most traditional on-site setups, giving peace of mind in an era of cyber threats.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud backups and geographically distributed data centers mean your critical data and applications stay safe from local disasters. Recovery is faster, ensuring minimal downtime and sustained operations.
- Global Reach with Local Experience: Easily deploy applications across worldwide data centers to provide low-latency, high-performance experiences for users everywhere, capturing new markets with ease.
- Automatic Updates: No more manual patching or software upgrades—cloud services update automatically in the background, keeping your systems cutting-edge and secure without interrupting your workflow.
Conclusion
On-demand, scalable, and easily upgradable computing resources mean no more purchasing and maintaining pricey on-premises infrastructure or worrying about regular upgrades. With improved team efficiency and greatly shortened time-to-market, cloud computing becomes an increasingly valuable business asset. The considerable effort required to manage a traditional on-premises infrastructure is no longer an issue, as organizations can quickly acquire and scale cloud services.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: