Over the past few years, chatbots have revolutionized how people interact with technology, serving millions of users across customer service, content automation, language assistance, and even code generation. These virtual agents are powered by advanced language models such as GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, each capable of processing and generating text that is both relevant and surprisingly human-like. What sets these AI chatbots apart is their sophisticated techniques built into their foundation — like an attention mechanism for context awareness, transfer learning for scaling expertise, and continuous training to fine-tune results over time.
In fact, according to a recent study from Exploding Topics, the global AI chatbot market is projected to grow by $46.64 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 24.53% during the forecast period (2021 – 2029). If you’re curious about the magic happening behind the scenes, this blog is your gateway. We’ll break down the process, look at practical techniques every step so you can create your own digital conversational partner from scratch.
Process To Develop an AI Chatbot In Java: Step-by-Step Guide [2025]
Building and deploying a large-scale AI system like this involves numerous challenges. Creating a robust infrastructure to rival top services like ChatGPT is no small feat. However, thanks to the abundance of open-source tools and resources available today, it’s possible to develop highly functional and reliable chatbot applications. Many of these tools boast impressive progress, are easy to use, modular, and simple to integrate — qualities that significantly enhance and speed up the development journey.
Here’s a detailed yet approachable roadmap to develop a robust chatbot, with actionable programming tips sprinkled throughout.
Step 1: Set Up Your Java Development Environment
Begin by preparing your tools:
- Install JDK: Download and install the latest Java Development Kit (JDK 17 or above recommended). This ensures you have the core Java language and runtime.
- Integrated Development Environment (IDE): Use IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse for efficient coding, debugging, and project management.
- Use a Build System: Maven or Gradle to automate dependency management. Create a project scaffold (mvn archetype:generate for Maven) to keep code organized and scalable.
- Manage Dependencies: In your pom.xml (if Maven), add chatbot-relevant libraries upfront. For example, for OpenAI GPT integration or when working with ChatGPT integration Services, include the required dependencies to enable smooth communication between your Java application and the API.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.theokanning.openai-gpt3-java</groupId>
<artifactId>client</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1</version>
</dependency>This ensures smooth packaging and dependency resolution.
Step 2: Initialize Your Chatbot Project and Libraries
Import essential chatbot libraries like Program AB for AI/ML processing or OpenAI API clients if you want GPT-powered language capabilities.
Configure your pom.xml like this to include the OpenAI Java SDK:
Create a clean folder structure:
text
src/
main/
java/
com/
yourdomain/
chatbot/
Chatbot.java
resources/
aiml/Add necessary imports to your core chatbot class. For example, if you’re using AIML:
java
import org.alicebot.ab.Bot;
import org.alicebot.ab.Chat;
import org.alicebot.ab.MagicBooleans;If relying on OpenAI or other APIs, also import Java HTTP clients or SDKs.
Step 3: Build the Basic Chatbot Loop
Start simple with a console app that can take inputs and respond:
public class ChatbotApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Bot bot = new Bot("super", "src/main/resources");
Chat chatSession = new Chat(bot);
System.out.println("Chatbot ready! Type 'exit' to quit.");
while(true) {
System.out.print("You: ");
String input = scanner.nextLine();
if("exit".equalsIgnoreCase(input)) break;
String response = chatSession.multisentenceRespond(input);
System.out.println("Bot: " + response);
}
scanner.close();
}
}This loop takes input, sends it to the AIML bot engine, and prints replies. It’s the backbone of your chatbot.
Step 4: Add Advanced AI/NLP with LLMs
Elevate your chatbot with AI by connecting to large language models (LLMs).
Using OpenAI API with Java:
OpenAiService service = new OpenAiService("YOUR_API_KEY");
CompletionRequest completionRequest = CompletionRequest.builder()
.model("gpt-4o-mini")
.prompt("User: Hello! Bot:")
.maxTokens(50)
.build();
String answer = service.createCompletion(completionRequest).getChoices().get(0).getText().trim();
System.out.println("Bot: " + answer);Hybridize by letting AIML handle FAQs and GPT handle open-ended questions for a smoother experience.
Step 5: Build and Manage the Knowledge Base
Structure your chatbot’s brain effectively:
- Organize AIML files with clear categories for intents.
- Write patterns for possible questions and matching templates for answers.
Example AIML snippet:
<category>
<pattern>HELLO</pattern>
<template>Hello! How can I assist you today?</template>
</category>Reload updates dynamically without restarting the app to handle evolving knowledge bases.
Step 6: Handle Conversational Context and Multi-Turn Dialogue
Basic chatbots respond statelessly—to improve:
- Track user context with objects or session variables.
- Store previous interactions for meaningful follow-ups.
For instance, maintain a Java Map<String, String> for user state:
Map<String, String> sessionContext = new HashMap<>();
sessionContext.put("lastQuestion", currentUserInput);Use this to tailor replies based on recent user history.
Step 7: Deploy Your Java Chatbot
Transition your console chatbot into a web service:
- Use Spring Boot to expose REST endpoints:
@RestController
public class ChatBotController {
private Chat chatSession;
public ChatBotController() {
Bot bot = new Bot("super", "resources");
this.chatSession = new Chat(bot);
}
@PostMapping("/chat")
public String chat(@RequestBody String userMessage) {
return chatSession.multisentenceRespond(userMessage);
}
}- Package as a JAR or Docker container and host on cloud platforms or your own servers.
- Integrate with messaging platforms through webhooks and APIs for Slack, Telegram, or WhatsApp.
Step 8: Test and Debug Thoroughly
- Simulate varied user inputs to identify edge cases.
- Log responses and errors with SLF4J or Log4j.
- Use unit testing frameworks like JUnit for core logic tests.
- Monitor runtime performance and fix bottlenecks.
Step 9: Maintain and Iterate
- Regularly update AIML content or retrain AI models based on user feedback.
- Analyze logs for common queries or breakdowns.
- Personalize chatbot responses by adding user profiles or preferences.
- Expand functionality by integrating databases, analytics, or voice interfaces.
Understanding AI Chatbot In Java: Benefits & Use Cases
In the last couple of years, the applications of AI chatbots have grown tremendously, enabling companies to streamline processes, provide 24*7 technical support, and improve user satisfaction. With its versatility and strong ecosystem, Java is an appropriate language of choice for AI Chatbot Development and overall chatbot creation. This is why we have prepared a comprehensive guide to help you develop a chatbot in Java, focusing on each step in detail. But, before that, let us understand the basics first.
Why Choose Java for AI Chatbot Development?
Why opt for Java when there are so many languages and frameworks to choose from?
Java stands out from others for its robust ecosystem, strong support for object-oriented design, and long-standing libraries that range from basic scripting to advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML). It’s also widely used in delivering Machine Learning Development Services, making it a language trusted by developers for everything from simple prototypes to complex, production-grade software.
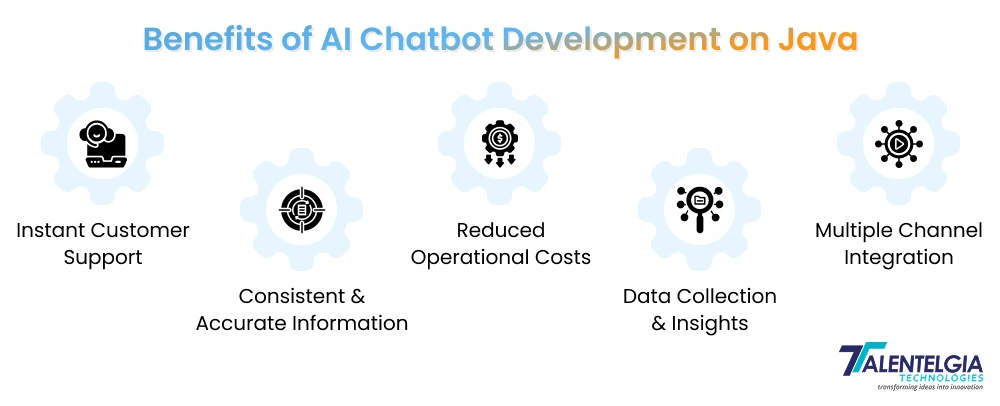
Java chatbots can power websites, internal enterprise tools, mobile apps, and customer support solutions. With Java, you can:
- Instant Customer Support: Automatic responses mean users get help 24/7, regardless of time zones or holidays, improving satisfaction and trust.
- Consistent and Accurate Information: Chatbots draw on your approved knowledge base, guaranteeing every answer reflects the most current and accurate company information—no more outdated or conflicting advice.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By automating routine inquiries and workflows, AI chatbots trim support costs and allow your human teams to focus on genuinely complex or creative tasks.
- Data Collection and Insights: Every conversation helps you understand user needs and trends, giving you feedback to improve products, content, or services.
- Seamless Integration with Multiple Channels: Serve users on your website, messaging apps, or internal portals with the same high-quality responses, wherever they start the conversation.
What are The Key Use Cases of AI Chatbots In Java?
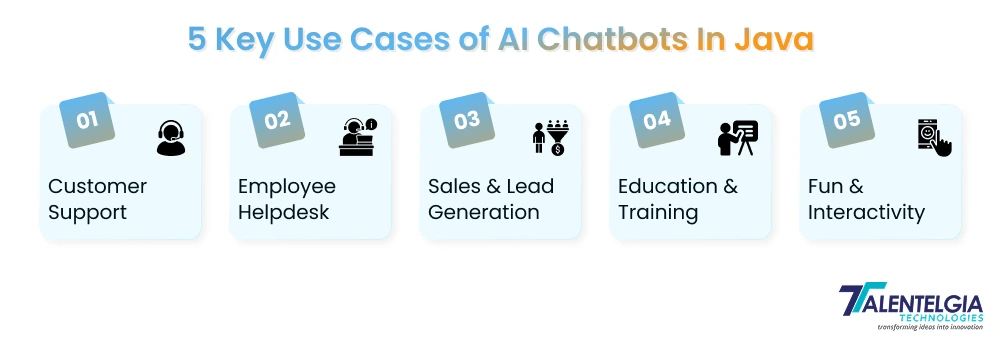
Building a chatbot in Java isn’t just about code—it’s about solving real problems. Common use cases include:
- Customer Support: Answer frequent questions, guide users, and help resolve issues in real-time, 24/7.
- Employee Helpdesks: Provide self-service for HR, IT, or operations queries inside organizations.
- Sales and Lead Generation: Proactively engage users, qualify leads, and recommend products.
- Education and Training: Act as an intelligent tutor or onboarding assistant, available anytime.
- Fun and Interactivity: Develop hobby projects, games, or playful personal assistants for learning and experimentation.
Wrapping It Up!
Despite having a functional system, there is still room for more improvements, based on the software and hardware used. Nonetheless, considering the available resources, it can still offer a reasonable service to a small number of users. It is important to remember that it is difficult to reach the level of performance that systems like ChatGPT provide, as it is a costly model to run and requires appliances to a particular tier to support it.
And for the systems that is described in this post, small or even medium-scale solutions are certainly scalable, but it involve much more advanced technology and perhaps, leveraging some of the system’s architecture for large-scale solutions. By combining these steps with Java’s reliability and powerful ecosystem, we can help you develop an AI chatbot for your business, that is not only functional but also responsive and expandable.
For AI Integration Services, Contact Us Today!


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: