The current cyber threats are more insidious and prevalent than ever before. Whether it is a phishing scam, ransomware, or an advanced persistent threat (APT), businesses continue to wage a tireless war against the threats that threaten to halt business, steal sensitive data, and lead to millions of dollars in damages. While conventional security systems are important, they are to some degree reactive; they identify and respond to attacks and threats only after they inflict damage.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) appears here as the disruptor. AI is transforming cybersecurity from a defense to an offense by monitoring large datasets in real-time to identify anomalies and training on new, evolving types of attacks. Find out how AI in Business enables businesses to be one step ahead of cybercriminals. Whether it’s recognizing abnormal login patterns, noticing insider threats, or blocking zero-day attacks, AI-powered threat detection gives companies a strong advantage over would-be cyber intruders.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into how AI is changing the game in threat detection, some of its primary uses as they pertain to cybersecurity, things to love about the technology, and what the future of AI-enabled security will look like in 2025 and beyond. Let’s get started:
What Is AI In Threat Detection?
AI threat detection applies artificial intelligence technologies, primarily machine learning (ML) and advanced analytics, to automatically identify security threats before they have a detrimental effect. Unlike previous approaches, which may rely on manual monitoring or static rule-based systems to identify unusual behavior, AI-powered detection constantly learns from user activity, network traffic, and system events. This allows businesses to rapidly identify outliers that might signal phishing, malware, insider attacks, or other nefarious activity. By automating the detection of these threats, AI not only succeeds in minimizing human error but also permits businesses to act on new threats in real-time and, in this context, represents an operational tool for modern cybersecurity efforts.
Why Traditional Methods Of Threat Detection Are Failing?
Today’s hackers are more sophisticated, nimble, and advanced than what security systems of the past were built to address. Outmoded methods of defense leave organizations at risk because they can’t stay in step with attackers’ always-changing methods. Some of the greatest failures are:
Narrow focus of signature-based solutions – Traditional systems can hunt known malware signatures, but they cannot see emergent or polymorphic malware or new types of cyber threats.
So many false positives – Security teams are bombarded with alerts generated by inflexible, rules-based monitoring systems, leading to alert fatigue and a flood of actual threats slipping through the cracks.
Sophisticated attacks – Nation-state actors and ransomware-as-a-service groups utilize far more advanced attack techniques that circumvent perimeter-based security.
More intelligent phishing attempts – Thanks to Generative AI, phishing emails are more personal and therefore more realistic-looking instead of obnoxiously untargeted, making it easier for them to bypass common spam filters.
The perimeter trust model is flawed – Traditional security technology expected the threats to come from outside, leaving the inside lateral movement and insider threats mostly unmitigated.
Ultimately, traditional tools can’t keep up with modern cyber threats because they simply can’t provide the pace, precision, and flexibility required to stop them, leading to a future reliant on AI for threat detection.
How Does AI In Threat Detection Work?
AI in cybersecurity isn’t just “there to spot threats”; it learns, adjusts, and responds quicker than any reactive system. AI is transforming modern threat detection. By analyzing massive amounts of data patterns to notice the full extent of the risk or recognize the patterns that could indicate an on security, it’s possible to identify risks that human teams or legacy tools might miss. Phishing defence, here’s how AI is driving smarter threat detection:
1. Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection, particularly based on machine learning, is one of the most common applications of AI in cybersecurity. For example, an AI system could examine millions of authentication logs of servers, applications, and endpoints. It can then compare that activity to previous attempted breaches and spot commonalities, for example, a spike in failed login attempts followed by a weird spike in network traffic. If the system experiences something like a previous brute force attempt or a credential-stuffing attack, it can alert security teams sooner and better contain another horse escaping the barn. Companies such as Microsoft and IBM already utilize AI-based analytics to enhance SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems for this task.
2. AI-Powered Phishing Detection
Phishing is one of the most successful attack types, and advanced ones are often overlooked by filters. AI can be a standout here by parsing the natural language and behavioral insights sent in emails, SMS, or chat apps. For instance, it could flag an email that induces fake urgency (such as “reset your password now”) or pretends to be a CEO ordering employees in finance to wire money. Google has said that its AI models are stopping more than 100 million phishing attempts in Gmail every day by recognizing these subtle patterns that a person might miss.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Produced Threat Context (including Remediation)
Even more sophisticated systems are moving further than detection to context-awareness and response plans. With generative AI, tools can summarize what remains an active threat, describe how attackers might use it, and even suggest step-by-step remediation. So, for example, if a zero-day was discovered, an AI system might produce guidance on how to patch, suggest temporary firewall rules, or recommend the isolation of vulnerable devices. There are already providers such as CrowdStrike and Palo Alto Networks that are deploying AI-driven platforms that provide this level of prescriptive security assistance in real time.
4. Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has become one of the most formidable applications for machine learning, more so with the advent of large language models (LLMs). In cybersecurity, NLP is the magic that lets AI systems read, understand, and analyze human language like we do—but at a scale and speed no human team can come close to.
This is what makes NLP an extremely valuable weapon for spotting out fake phishing emails, for example, and social engineering attempts, and pieces of suspicious content, overcoming the traditional filters. By processing massive volumes of text-based data, such as emails, chat logs, and business documents, NLP-driven threat detection systems can identify unusual patterns, harmful intent, or even insider threats.
Simply put, NLP provides cybersecurity teams with a more effective lens to be able to detect language-based attacks in real time and safeguard organizations against ever-changing threats.
Key Components Of AI In Threat Detection
AI in threat detection isn’t simply algorithms doing math calculations; it is multiple smart technologies working together to get the upper hand on cybercriminals. In this article, we look at the essential technologies that enable AI-based security:
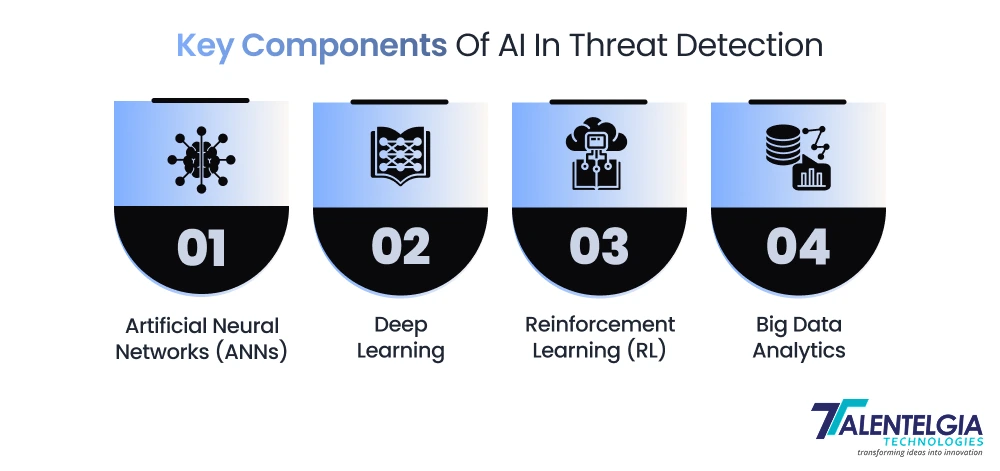
- Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
Imagine ANNs as digital neurons with ever-changing weights. They mirror the method our brain builds up patterns and uses them for cybersecurity. ANNS can identify anomalous behavior in network traffic or user activity by processing supervised and unsupervised data. That gut feeling of “something just doesn’t look right” that we humans get? ANNs replicate it at scale.
- Deep Learning
If ANNs are the brain, deep learning is the powerhouse, going through several layers deeper. It has the potential to trawl massive amounts of data and reveal hidden insights, sort of like finding a needle in a haystack. In cybersecurity, deep learning is good at finding malware finding phishing attempts, and it can even analyze pictures or videos to pick out the weird stuff it finds interesting with some sophisticated threat analysis.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
Here’s where it gets interesting. Reinforcement learning is what teaches AI systems to make decisions based on rewards and penalties. In shorter terms, the system “learns from experience.” For threat detection, RL helps AI to select the smartest response, such as blocking suspicious behavior, quarantining a device, or notifying a security team.
- Big Data Analytics
Cybersecurity is a data-heavy game. From network logs to user behavior to real-time threat feeds, it’s simply too much information for humans to digest. And AI systems can process this ocean of data faster than ever before, thanks to big data analytics. The result? Quicker, smarter, and much closer to true detection of threats before they explode.
Threat Detection Implementation Strategies
Cybersecurity is a moving target these days—hackers change tactics daily, and older static defenses no longer suffice. To go beyond, companies should have a layered strategy combining state-of-the-art AI systems with human knowledge. The trick is not merely detecting threats but reacting to them immediately, even if they’re zero-day attacks or the tricks of the most-skilled hackers.
Here are examples of how using AI to power threat detection can succeed:
- Integration with Existing Security Systems
AI doesn’t work in a vacuum; it must be able to integrate with the existing security tools seamlessly. AI-infused detection platforms can connect through an API or middleware with your regular SIEM, firewalls, and endpoint protection solutions. This provides optimal information sharing, faster alerts, and accurate detection in an unobtrusive way.
And now, many companies are embracing hybrid threat detection models that incorporate AI-driven analytics with rule-based monitoring. This approach combines the best of two worlds – where AI learns from new threats, while the existing systems enforce the proven set of rules.
- Real-Time Processing and Analysis
With cyberattacks, it’s all about timing. AI threat detection in real-time uses machine learning and streaming to identify suspect activity on the fly. For instance, abnormal login attempts, spikes in network traffic, or unauthorized file transfers can be alerted on immediately, giving security teams the upper hand in stopping attacks before they take off.
Edge computing is also a factor in this, for example, enabling quicker analysis closer to the source of the data (such as IoT devices or remote offices), cutting out lag in response times.
Also Read: Best Cybersecurity Practices for Small and Medium Businesses
Specific Applications Of AI In Threat Detection
AI in cybersecurity is no longer a “nice-to-have”; it is a core defense in all spheres of business. Here are three key areas in which AI and machine learning are changing the way we detect threats:
1.Network Security
Network security AI solutions continuously analyze the traffic for anomalies and attack signatures. Using machine learning, they can differentiate between normal activity and suspicious activity (like the spread of malware, exfiltration of data, or attempts to brute-force logins).
- Anomaly detection – detects odd behavior that might be a sign of intrusion.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) – monitor the traffic to see if there is anything unusual coming in.
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) – instead of just spotting, it blocks threats as they happen.
- Large players such as Cisco and Palo Alto Networks are already employing AI-enhanced IDS/IPS to catch attacks before they impact the valuable stuff.
2.Endpoint Security
The endpoints, laptops, mobile devices, and IoT sensors, are frequently the weakest points in an organization. AI-based endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems observe user behavior, detect malware, and respond automatically. For example, if ransomware begins to encrypt files, AI can immediately quarantine the device to prevent further spread.
Firms like CrowdStrike and SentinelOne have developed AI-first platforms focused on protecting the endpoint from known and unknown threats.
3.Fraud and Anomaly Detection
Sectors like banking, e-commerce, and fintech rely on AI to thwart fraud long before it can do any harm. AI models scrutinize millions of transactions in real time and detect suspect activity like new and atypical spending patterns or the creation of fake accounts and attempts at identity theft.
For example:
- In financial services, AI can uncover suspect payment patterns that may identify a fraudster.
- In retail and e-commerce, it can limit fraudulent transactions and chargeback fraud.
- With its capacity to identify fraud at scale, AI-based anomaly detection has emerged as a mission-critical application for protecting customer trust and maintaining data security.
Conclusion
Cybercriminals are going to be smarter, and there’s no way traditional defense measures can keep up anymore. And that’s where AI-powered threat detection comes into play. From identifying phishing attempts that land in your inbox to tracking suspicious behavior across entire networks, AI can identify patterns that human eyes are likely to miss. It operates in real time, it learns constantly, and provides an additional layer of security that only strengthens with new data points. Now, that also means less guesswork for businesses, quicker response times, and more robust defense against the latest and most complex attacks. When it comes to the future, AI isn’t just something nice to have — it’s turning into the cornerstone of modern cybersecurity.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: